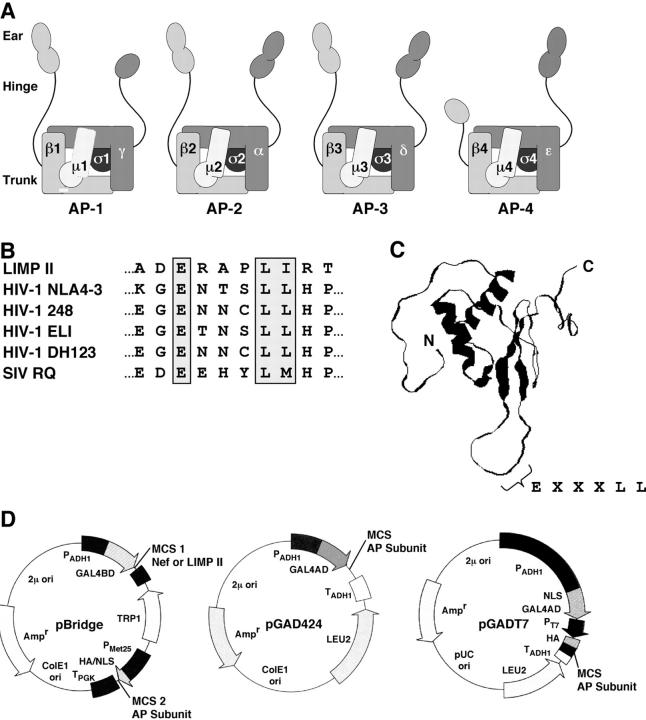
Figure 1.
Adaptors, signals, and plasmids used in this work. (A) Schematic representation of the heterotetrameric adaptor protein (AP) complexes. The designations of the generic subunits of each complex are indicated. The following subunits occur in various isoforms encoded by different genes, as indicated in parentheses: γ (γ1, γ2), μ1 (μ1A, μ1B), σ1 (σ1A, σ1B, σ1C), α (αA, αC), β3 (β3A, β3B), μ3 (μ3A, μ3B), and σ3 (σ3A, σ3B). The arrangement of the subunits was modeled after the crystal structure of the AP-2 core (Collins et al., 2002). The trunk, hinge, and ear domains of the large subunits are indicated. (B) Sequences of the dileucine-based sorting signals from LIMP-II and variants of HIV-1 and SIV Nef. The critical glutamate, leucine–leucine, leucine–isoleucine, and leucine–methionine residues are boxed. (C) NMR structure of HIV-1 Nef (BH10 isolate). The structure shown corresponds to the first of 40 structures determined by multidimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy (Grzesiek et al., 1997). The locations of the NH2 and COOH termini, and of the EXXXLL sequence, are indicated. (D) Yeast expression plasmids used in two- and three-hybrid assays. The pBridge plasmid expresses two proteins, GAL4BD fused to Nef or the LIMP-II cytosolic tail (multiple cloning site 1, MCS 1) and an AP subunit (MCS 2). The pGAD424 and pGADT7 plasmids drive high-level expression of GAL4AD fused to another AP subunit.