Abstract
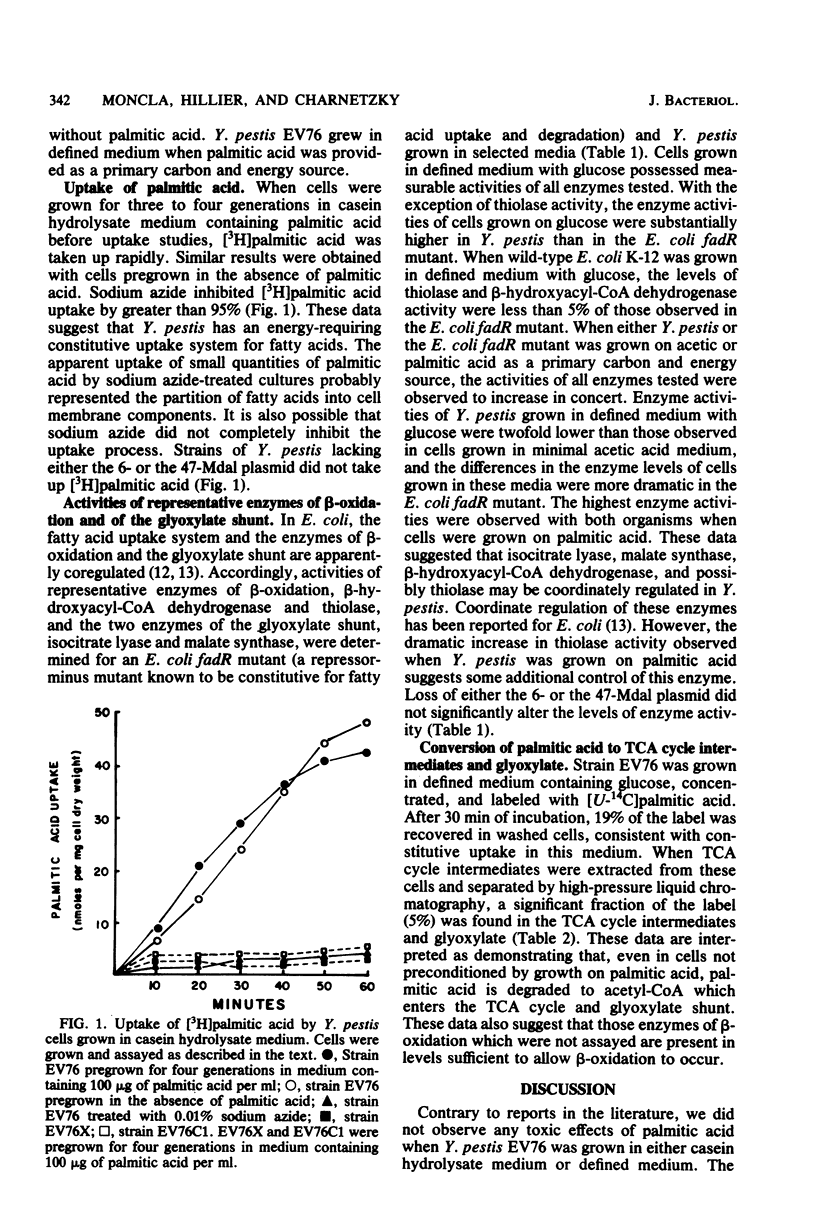
Yersinia pestis was found to utilize palmitic acid as a primary carbon and energy source. No inhibition of growth by palmitic acid was observed. Comparison of palmitic acid uptake by cells pregrown either with or without palmitic acid demonstrated that fatty acid uptake was constitutive. High basal levels of two enzymes of beta-oxidation, beta-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase and thiolase, and the two enzymes of the glyoxylate shunt, isocitrate lyase and malate synthase, were found in cells grown in defined medium with glucose. Elevated levels of all four enzymes were found when cells were grown with acetate as a primary carbon and energy source, and even higher levels were observed when palmitic acid was provided as a primary carbon and energy source. High-pressure liquid chromatography was used to demonstrate that, in the presence of glucose, uniformly labeled [14C]palmitic acid was converted to intermediates of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and glyoxylate shunt. Pregrowth with palmitic acid was not required for this conversion. Strains lacking the 6- or the 47-megadalton plasmid did not take up [3H]palmitic acid but did possess levels of enzyme activity comparable to those observed in the wild-type strain.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. Interconversion of Purine Mononucleotides in Pasteurella pestis. Infect Immun. 1970 May;1(5):446–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.5.446-454.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier H. B. Letter: A note on the molar absorptivity of reduced Ellman's reagent, 3-carboxylato-4-nitrothiophenolate. Anal Biochem. 1973 Nov;56(1):310–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisler D. M., Von Metz E. K. Anti-Pasteurella pestis factor. 3. Effects of fatty acids on Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1767–1773. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1767-1773.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., KUPFERBERG L. L., SMITH J. L. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. III. Effects of calcium ions on the growth of virulent and avirulent strains of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1959 Mar;77(3):317–321. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.3.317-321.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsworth G. R., Kochan I. Secretion of antimycobacterial fatty acids by normal and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.170-177.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier S. L., Charnetzky W. T. Rapid diagnostic test that uses isocitrate lyase activity for identification of Yersinia pestis. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Apr;13(4):661–665. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.4.661-665.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier S., Charnetzky W. T. Glyoxylate bypass enzymes in Yersinia species and multiple forms of isocitrate lyase in Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):452–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.452-458.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein K., Steinberg R., Fiethen B., Overath P. Fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli. An inducible system for the uptake of fatty acids and further characterization of old mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Apr;19(3):442–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01334.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Bohlander M., Nunn W. D. Elevated levels of glyoxylate shunt enzymes in Escherichia coli strains constitutive for fatty acid degradation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):720–725. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.720-725.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melching L., Vas S. I. Effects of serum components on gram-negative bacteria during bactericidal reactions. Infect Immun. 1971 Jan;3(1):107–115. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.1.107-115.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okudaira H., Kataoka T., Okada H., Furuse-Irie R., Kawachi S. Cytotoxic factor demonstrated in lymph node extract. J Biochem. 1970 Sep;68(3):379–394. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overath P., Pauli G., Schairer H. U. Fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli. An inducible acyl-CoA synthetase, the mapping of old-mutations, and the isolation of regulatory mutants. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):559–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL A. W., ABBOT A. The function of glycerol, cholesterol and long-chain fatty acids in the nutrition of Mycoplasma mycoides. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:201–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. COMPARATIVE PHYSIOLOGY OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE AND L-TYPE ORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Jun;28:97–125. doi: 10.1128/br.28.2.97-125.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer W. B., Davis C. L., Cohn M. L. Pathogenicity of transparent, opaque, and rough variants of Mycobacterium avium in chickens and mice. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Oct;102(4):499–506. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Egan P. A., Chute H. T., Nunn W. D. Regulation of fatty acid degradation in Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of strains bearing insertion and temperature-sensitive mutations in gene fadR. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):621–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.621-632.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks G., Shapiro M., Burns R. O., Wakil S. J. Control of fatty acid metabolism. I. Induction of the enzymes of fatty acid oxidation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):827–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.827-836.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


