Figure 1.
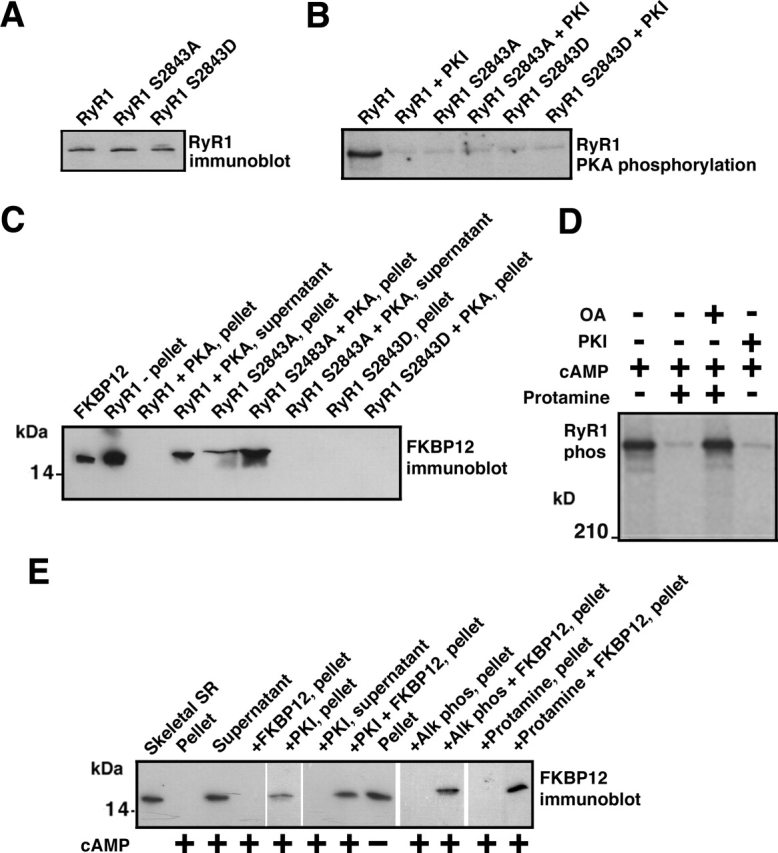
FKBP12 binding to RyR1 is regulated by PKA phosphorylation of RyR1-Ser2843. (A) Immunoblot showing that equivalent amounts of WT and mutant (RyR1-S2843A and RyR1-S2843D) RyR1 were expressed in HEK293 cells. (B) Autoradiograph showing PKA phosphorylation of RyR1 using γP32-ATP (PKI5–24 was used to show specificity of the kinasing reaction). Alanine substitution identified Ser2843 as the unique PKA phosphorylation site on RyR1. (C) Immunoblot showing binding of FKBP12 to WT and mutant RyR1, assessed by centrifugation (FKBP12 cosediments with RyR1) and FKBP12 immunoblotting. FKBP12 does not bind to RyR1-S2843D, which mimics constitutively PKA-phosphorylated RyR1. (D) Autoradiograph showing that activation of PKA bound to RyR1 with cAMP causes phosphorylation of the channel, which is inhibited by the PKA inhibitor PKI5–24. Activation of PP1 bound to the channel with protamine causes dephosphorylation of the channel, which is blocked by okadaic acid (OA). (E) FKBP12 immunoblot showing that cAMP-induced PKA phosphorylation of RyR1 dissociates FKBP12 from the channel complex. FKBP12 cannot bind to the PKA-phosphorylated channel, but dephosphorylation of the channel with alkaline phosphatase (or by activating bound phosphatases with protamine) allows subsequent rebinding of FKBP12 to the channel, as assessed by cocentrifugation.
