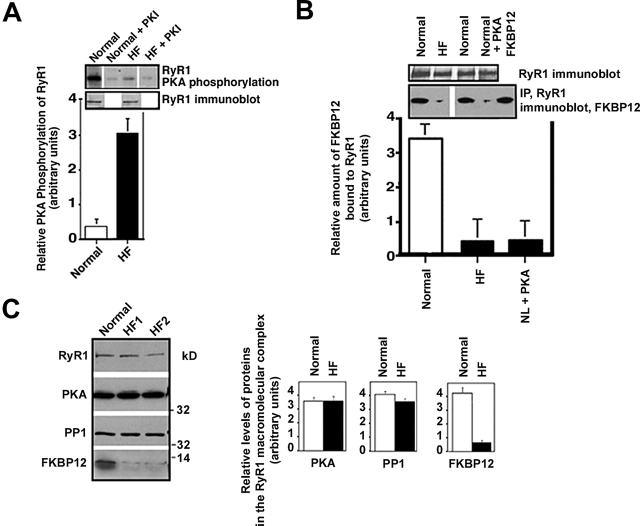
Figure 3.
RyR1 PKA hyperphosphorylation in HF skeletal muscle. (A) PKA phosphorylation of RyR1 was measured in skeletal muscle homogenates from control normal dogs and dogs with pacing- induced HF. Equivalent amounts of RyR1 protein were used in each kinasing reaction, as shown by immunoblotting. The relative PKA phosphorylation of RyR1 from skeletal muscle homogenates from normals (n = 2) and HF animals (n = 5) was determined by dividing the specific phosphorylation signal by the amount of RyR1 protein (determined by immunoblotting and densitometry). Results are expressed as the inverse of the PKA-dependent [γ-32P]ATP signal ± the SD of the mean. (B) The amount of FKBP12 bound to RyR1 was assessed by coimmunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting. (C) Representative immunoblots are shown for components of the RyR1 macromolecular complex: RyR1, PKA, PP1, and FKBP12 using samples from normal (n = 2) and HF animals (n = 5). Protein levels were quantified using densitometry of immunoblots. Results are expressed as the relative amount of each of the components of the RyR1 macromolecular complex corrected for the amount of RyR1 in each immunoprecipitation. Error bars are SD of the mean.