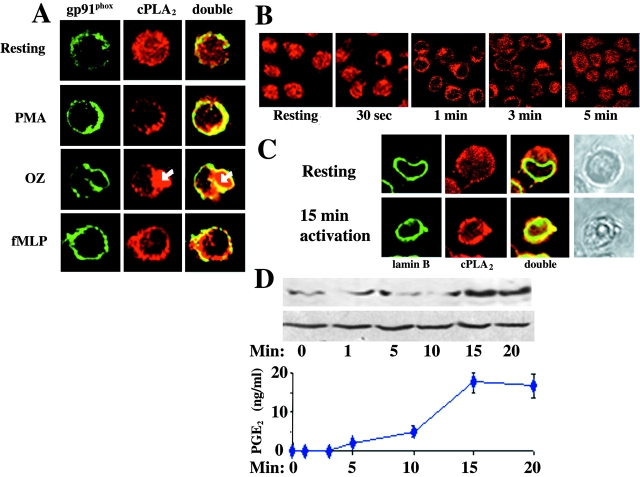
Figure 6.
Subcellular localization of cPLA2 in stimulated granulocyte-like PLB-985 cells. (A) Granulocyte-like PLB-985 cells before and after stimulation with 1 mg/ml OZ, 5 × 10−7 M fMLP for 1 min or 50 ng/ml PMA for 3 min at 37°C were fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with anti-cPLA2 and anti-gp91phox antibodies and then with cy3- and cy2-conjugated second antibodies, respectively. cPLA2 was found in the cytosol in resting cells and colocalized with gp91phox in the plasma membranes in stimulated cells. An engulfed OZ particle (stained in red as indicated by the white arrow) is surrounded by plasma membranes in which gp91phox and cPLA2 colocalized (×1,000). (B) The time course translocation of cPLA2 to cell periphery after stimulation with 5 × 10−7 M fMLP (×400). (C) Lamin B was labeled by anti–lamin B antibodies and then with cy2-conjugated second antibodies. cPLA2 colocalized with lamin B in nuclear membranes of stimulated cells with 5 × 10−7 M fMLP for 15 min (×1,000). (D) The kinetics ± SEM of PGE2 production (of three experiments, each in triplicates) and of cPLA2 translocation to the nuclear fractions (a representative immunoblot analysis of the three experiments) in 5 × 106 cells/ml granulocyte-like PLB-985 cells after stimulation with 5 × 10−7 M fMLP. 2 × 106 cell equivalent of nuclear fraction was applied in each lane. Equal amounts of the nuclear fractions were confirmed by detection of the levels of lamin B in each sample by immunoblot analysis.