Figure 1.
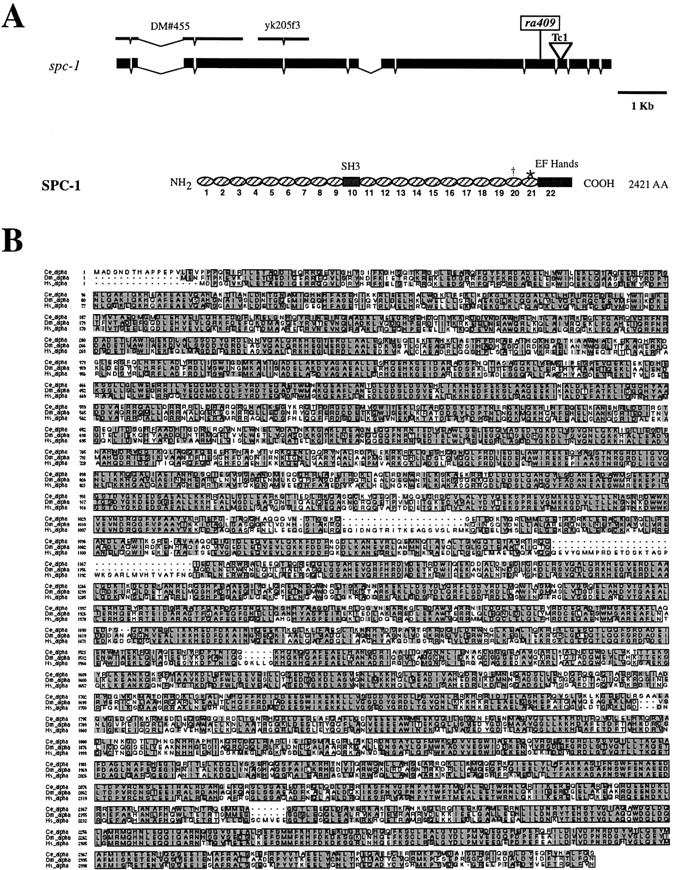
spc-1 encodes α spectrin. (A) The genomic structure of the spc-1 gene and the encoded protein structure. The exons are indicated by the black boxes, and the introns are indicated by the thin black lines. The nonsense mutation is shown (ra409), and the Tc1 insert is shown by the inverted triangle in the 10th exon. The cDNA clones used for generating dsRNA are shown above the genomic structure. Spectrin repeats are illustrated by ovals. The nonrepetitive domains are indicated by boxes. † and * indicate where the spc-1(ra409) mutation and the Tc1 introduce premature stop codons, respectively. (B) Deduced amino acid sequence of C. elegans α spectrin aligned to Drosophila and human nonerythroid α spectrin. The C. elegans α spectrin (Ce_α; sequence data available from GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under accession no. AAB53876) is 61% identical and 76% similar to Drosophila α spectrin (Dm_α; sequence data available from GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under accession no. P13395), and it is 57% identical and 72% similar to the human nonerythroid α spectrin (Hs_α; sequence data available from GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ under accession no. NP_003118). Identity is boxed, and similarity is shaded.
