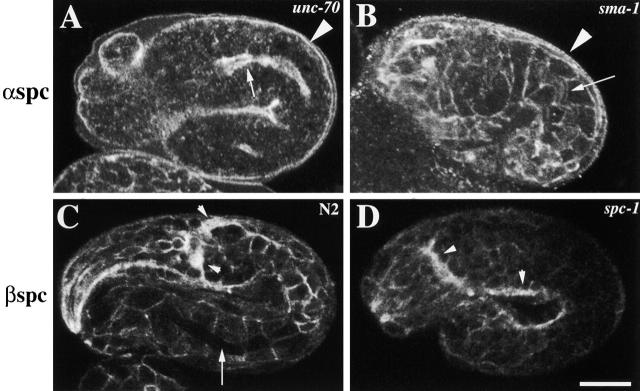
Figure 3.
α and β spectrin localization in spectrin mutants. Representative (A) unc-70(s1639) and sma-1(ru18) (B) embryos labeled with AS1 and examined by confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. In unc-70 (β spectrin) mutant embryos, (A) α spectrin fails to localize to the membrane except to the apical region of the intestine (arrow) and the hypodermis (arrowhead). (B) α spectrin localization is normal in sma-1 (βH spectrin) mutant embryos (the arrow indicates the apical region of the intestine, and the arrowhead indicates the apical region of the hypodermis). Wild-type (C) and spc-1(ra409) (D) embryos labeled with β spectrin antisera. (C) β spectrin localizes to the cell membrane of all cells including the nervous system (arrowheads). However, β spectrin does not localize to the apical region of the intestine (arrow) and hypodermis. (D) In the absence of α spectrin, β spectrin is not stably localized to the membrane as is seen by the faint immunofluorescence in the spc-1 mutant embryo. However, stronger β spectrin immunofluorescence is detected in the nervous system of spc-1 mutants (arrowheads). Bar, 10 μM.