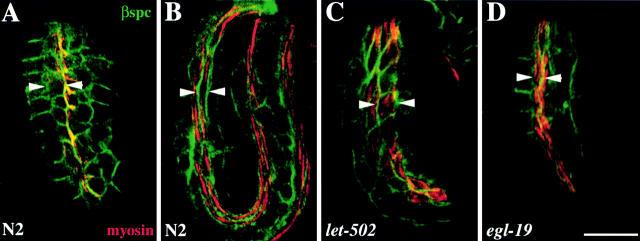
Figure 7.
Body wall muscle cells fail to undergo cell shape changes in the slow elongation mutants. Representative wild-type (A and B), let-502(h738) (C), and egl-19(st556) (D) embryos double labeled with myosin antisera (red) and β spectrin antisera (green). In wild-type embryos, the body wall muscle cells change shape from round to spindle-shaped cells. (A) Comma stage wild-type embryo showing the initial shape of the body wall muscle cells at the start of embryonic elongation. (B) Threefold wild-type embryo indicating the cell shape change that the body wall muscle cells undergo during embryonic elongation. (C) In the slow elongation mutants (let-502), the body wall muscle cells fail to undergo normal cell shape changes and remain similar to the body wall muscle cells in the wild-type comma stage embryo (C compared with A and B). (D) Normal cell shape changes occur in the Pat mutant, egl-19. Arrowheads indicate cell width. Bar, 10 μM.