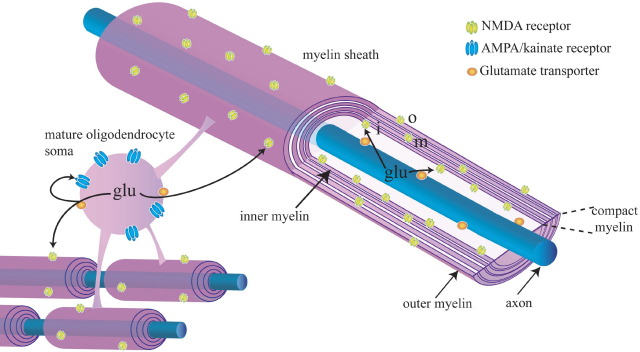
Fig. 3.
Receptor distribution defines the spatial segregation of damage expected when glutamate (glu) is released from axons and oligodendrocytes by reversal of uptake carriers (orange) in conditions of energy deprivation. Glutamate released from axons will activate NMDA receptors (yellow) on the inner wrap (i) of the myelin, leading to ion flux into the myelin and myelin damage. Glutamate released from oligodendrocytes will activate AMPA/kainate receptors (blue) on the soma (possibly leading to death of the soma) and also NMDA receptors on the inner and outer (o) wraps of the myelin.