Figure 1.
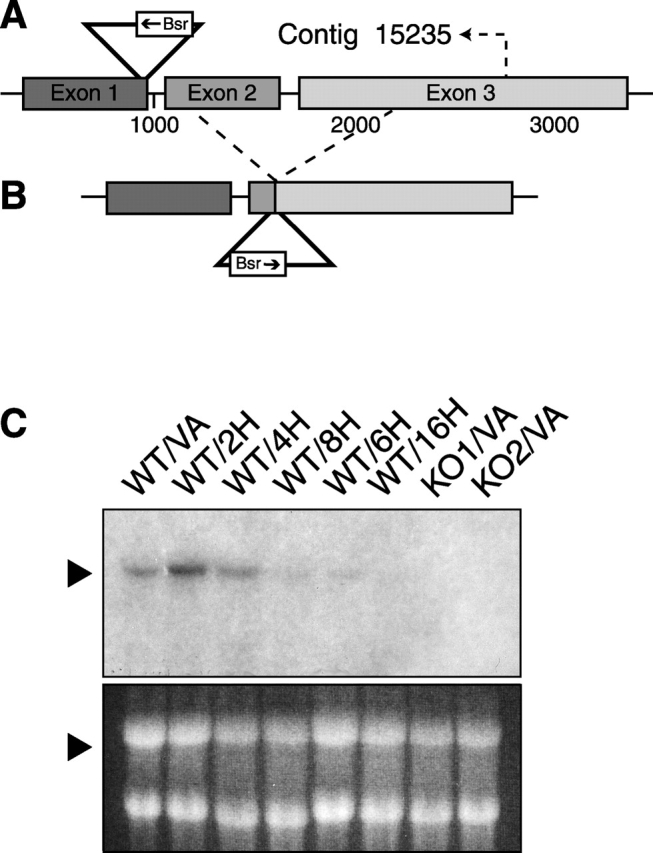
SadA locus and transcript. (A) SadA gene structure and plasmid insertion site. In REMI mutant 3IIG11, the transforming plasmid pUCΔBamBsr inserted at the 3′ end of the first exon, disrupting transcription of the remainder of the gene. Indicated at position 2790 is where the sequence of contig 15235 ends. (B) Structure of the knock-out construct. The plasmid pUCΔBamBsr containing genomic flanking sequences was inserted by homologous recombination so that the vector inserted in opposite direction as compared with the initial REMI mutant and resulted in the deletion of a 1-kb genomic sequence. (C) Northern blot analysis. In vegetative wild-type cells (WT/VA), the sadA transcript is ∼3.5 kb long. The presence of the transcript in developing wild type was tested after 2, 4, 6, 8, and 16 h starvation. Note that the gene is significantly down-regulated after 4 h starvation. The sadA transcript is absent in vegetative amoebae of two independent knock-out strains (KO1/VA and KO2/VA). As a loading control, the ethidium bromide–stained gel is shown.
