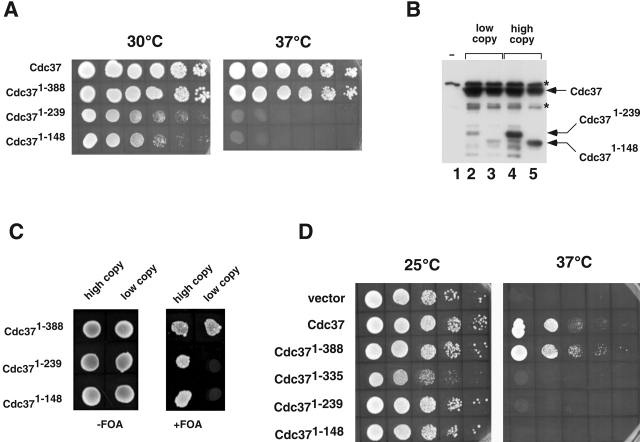
Figure 5.
The protein kinase–binding domain of Cdc37 is sufficient for viability. (A) Spot test analysis of cdc37Δ cells expressing wild-type (Cdc37) or truncated versions of Cdc37 as indicated in the figure. 10-fold dilutions of saturated cultures were plated (3 μl each) and incubated at 30°C and 37°C. (B) Western blot analysis of proteins eluted from Ni-NTA resin after incubation with extracts expressing vector alone (lane 1 or full-length histidine-tagged Cdc37 on a multicopy plasmid (lanes 2–5). Cdc371–239 was coexpressed with full-length Cdc37 on low copy number (lane 2) or high copy number plasmids (lane 4). Cdc371–148 was similarly expressed from low copy number or high copy number plasmids (lanes 3 and 5, respectively). Proteins that reacted with anti-His6 that bound nonspecifically to the resin are labeled with an asterisk. (C) Growth of cells expressing different forms of CDC37 from low copy or high copy number plasmids as indicated. Cells are shown spotted onto plates the absence or presence of 5-fluoroorotic acid (5-FOA) to counterselect for full-length Cdc37. (D) Spot test analysis of growth of cdc37–34 mutant yeast expressing truncated versions of Cdc37 as indicated. The cells were grown at 25°C or 37°C.