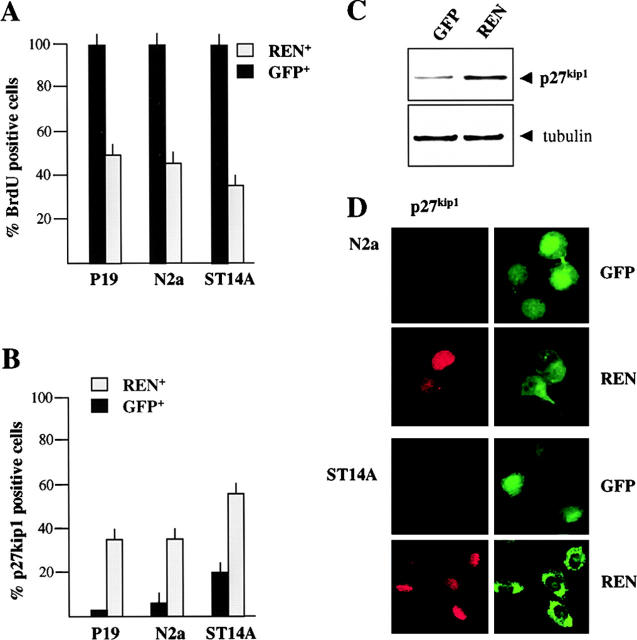
Figure 5.
REN induces cell growth arrest. (A) Cell growth arrest in P19, N2a, and ST14A cells transfected with expression vector pCXN2-REN-myc or with GFP expression vector. BrdU was added 24 h after transfection and detected after 2–24 h of incorporation. The percentage of BrdU incorporating cells in the REN+ or in the GFP+ population, was determined by coimmunostaining with anti-myc epitope and anti-BrdU antibodies or with anti-GFP and anti-BrdU antibodies and immunofluorescence microscopy. Average (± SEM) percentages of BrdU positive cells from three independent experiments performed in triplicate are shown. (B) Expression of p27Kip1 in control (GFP-transfected cells, GFP) and REN cDNA-transfected cells (REN) 48 h after transfection into P19, N2a, and ST14A cells. The percentage of p27Kip1 positive cells in the REN+ and in the GFP+ population, was determined by coimmunostaining with anti-myc epitope or anti-GFP antibodies and by immunofluorescence microscopy. Average (± SEM) percentages of p27Kip1 positive cells from three independent experiments performed in triplicate are shown. (C) Western blot analysis of p27Kip1 and α-tubulin expression in control (GFP-transfected, GFP) and REN cDNA-transfected N2a cells (REN), 48 h after transfection. (D) Exogenous expression of REN enhances p27Kip1 expression in N2a and ST14A cells. Confocal microscopy of coimmunostaining of p27Kip1 (red) and either myc epitope (green, REN) or GFP (green, GFP), in either GFP- (GFP) or REN-transfected (REN) cells, 48 h after transfection.