Figure 8.
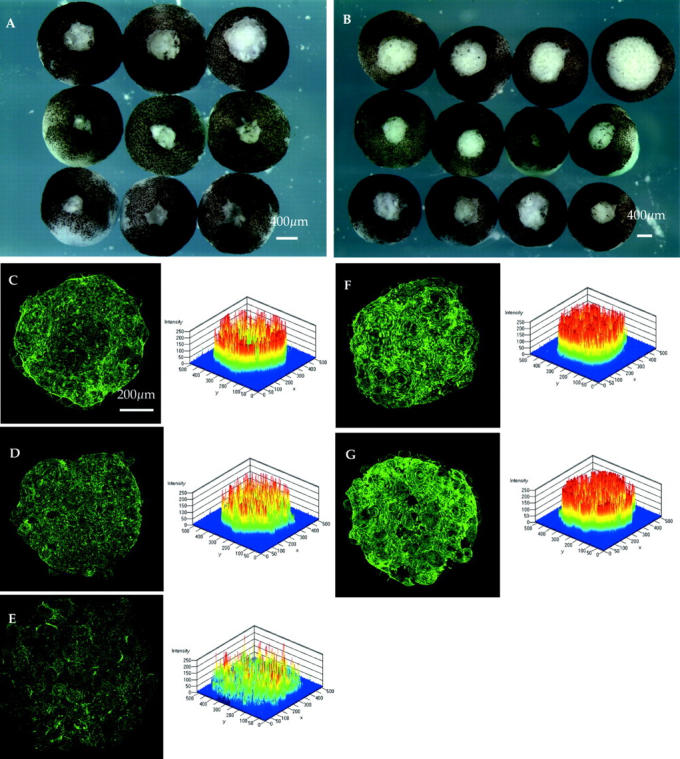
The effect of depletion of cdc42 mRNA on both wound-healing and cortical actin assembly in isolated animal caps, and the effects of injection of either cdc42 or plakoglobin mRNA on the effects of cdc42 depletion. (A) The effect of cdc42 depletion on healing of bases (top row) compared to controls (middle row). Injection of 400 pg cdc42 mRNA rescues the effect (bottom row). (B) Injection of 500 pg plakoglobin mRNA also rescues the effect (rows are the same as in A). (C–G) Pairs of images of isolated animal caps from the bases shown in A and B. On the left in each case are image stacks treated identically under the confocal microscope from Alexa 488–coupled phalloidin-stained caps, and on the right are quantitative measurements of pixel intensity across the image stack. (C) Uninjected; (D) cdc42 depleted; (E) plakoglobin depleted; (F) cdc42 depleted and injected at the two-cell stage with cdc42 mRNA (400 pg); (G) cdc42 depleted, and injected at the two-cell stage with plakoglobin mRNA (500 pg). Purse-strings and overall cortical actin depletion caused by depletion of cdc42 are rescued both by cdc42 and plakoglobin mRNAs.
