Figure 5.
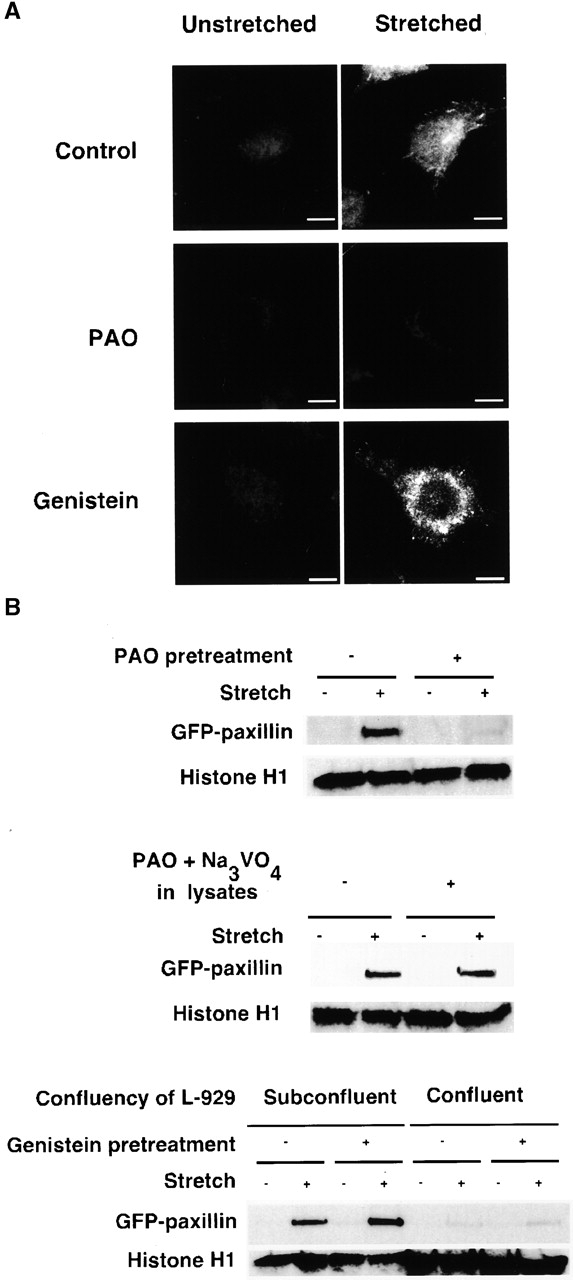
In vitro GFP paxillin binding to Triton X-100–insoluble cytoskeletons. (A) Triton X-100–insoluble cytoskeletons of L-929 cells in a StageFlexer system either unstretched (left) or stretched (10%; right) were incubated with 293-GFP-pax lysates (supplemented with 0.5 mM ATP, 2% BSA) for 2 min. After four washes with ISO (+) buffer, the bound complex of cytoplasmic proteins and cytoskeletons (Fig. 1) was fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde/ISO buffer. Stretched samples were relaxed after fixation, and the distribution of bound GFP paxillin was visualized with fluorescence microscopy (Olympus BX50 microscope with a 60×, 0.9 NA water immersion objective). PAO (20 μM; center) or genistein (100 μM; bottom) was added 10 min before permeabilization and stretching. (B) Triton X-100–insoluble cytoskeletons of L-929 cells in silicone dishes either unstretched or stretched by 10% were incubated with 293-GFP-pax lysates for 2 min. After four washes with ISO (+) buffer, the bound complex of cytoplasmic proteins and cytoskeletons (Fig. 1) were solubilized with 500 μl of SDS sample buffer (100 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 36% glycerol, 4% SDS, 10 mM DTT, 0.01% bromophenol blue). 50 μl of each sample was subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with antibodies to GFP (CLONTECH Laboratories, Inc.) and histone H1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.). PAO (20 μM; top), genistein (100 μM; bottom), or solvent (0.1% DMSO) was added 10 min before permeabilization and stretching. Triton X-100–insoluble cytoskeletons were prepared from 4 × 105 cells per dish with the exception of the confluent culture (four right lanes on bottom) where 1.2 × 106 cells per dish were used. Bar, 10 μm.
