Figure 1.
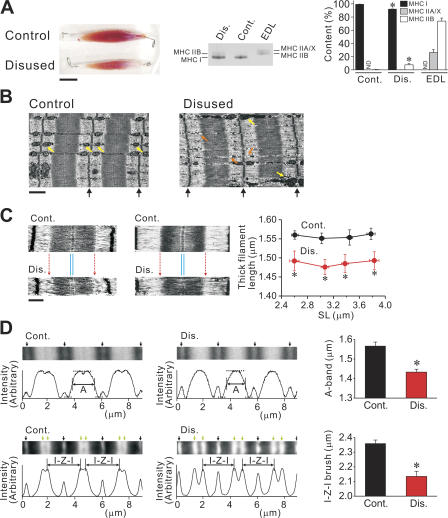
Disuse-induced morphological changes in muscle. (A) Changes in muscle size (left) and MHC expression (middle and right). Bar, 1 cm. Same animal was used in left and middle figures. Muscle bundles (∼30 mg) were solubilized and run for gel electrophoresis. EDL muscle was used as control for separation of MHC IIA/X and IIB. Cont., control without disuse; Dis., disused. MHC was run on 8% gel. In bar graph, ND indicates “not detectable” for densitometric analysis. *, P < 0.05, compared with the corresponding value for control soleus muscle. (B) Electron micrographs of longitudinal sections of intact soleus muscle, with (right) and without (left) disuse (taken from the same animal). SL ∼ 3.2 μm. Black arrows indicate the positions of the Z-line. Bar, 1 μm. Yellow arrows indicate mitochondria. Orange arrows indicate small granule vesicles. (C) Electron micrographs of longitudinal sections of sarcomeres in skinned single fibers, with (bottom) and without (top) disuse. Images at short (∼2.6 μm; type I) and long (∼3.2 μm; type I/II) SLs are shown (same animal used for each SL). Red dotted arrows indicate the position of the A/I junction in control sarcomere. Note similar thickness of the M-line in control and disused sarcomeres (indicated by thin blue lines) (see Fig. 4 B). Bar, 0.5 μm. Graph shows average thick filament length in control vs. disused fibers at various SLs (from eight animals; type I and I/II fibers pooled for disused group). *, P < 0.05, compared with control. (D) Fluorescence analyses of sarcomeres in skinned fibers, with and without disuse. Typical images and corresponding intensity profiles are shown. Top, A-band width measurement. Images: black arrows indicate the positions of the Z-line. Intensity profiles: horizontal dashed lines indicate the highest and lowest intensity values and vertical lines the midpoint of fluorescent intensity. The distance between vertical lines was defined as the average A-band width (noted as A). Bar graph summarizes the data from four animals (n = 10; type I and I/II fibers pooled for disused group). SL was 2.70 ± 0.07 and 2.78 ± 0.08 (P > 0.05) in control and disused muscle, respectively. Bottom, I-Z-I brush width measurement. Images: black arrows indicate the positions of the Z-line and green arrows the positions of the pointed end of the thin filament (Yasuda et al., 1994). The thin filament length was obtained by dividing the I-Z-I brush width (noted as I-Z-I) by a factor of 2. Bar graph summarizes the data from four animals (n = 6; type I and I/II fibers pooled for disused group). The value of the thin filament length in control muscle was similar to that reported previously with electron microscopy (Herzog et al., 1992). SL was 2.86 ± 0.05 and 2.73 ± 0.03 (P > 0.05) in control and disused muscle, respectively. *, P < 0.05.