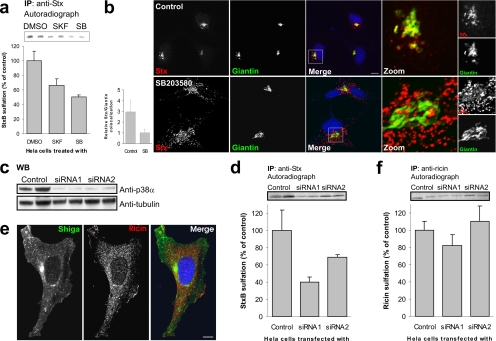
Figure 1.
p38 inhibition reduces transport of StxB, but not ricin, to the TGN. (a) HeLa cells were incubated with radioactive sulfate for 3 h, and the indicated inhibitors (SKF86002 and SB203580; 30 μM) or the carrier (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]; 0.1% final concentration) were present for the last 30 min. StxB was then added, and the incubation was continued for 45 min. StxB was immunoprecipitated from the lysates, and its degree of sulfation was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The band intensities were quantified and the average plotted with error bars showing deviations. The experiment was performed three times with duplicates. (b) HeLa cells were incubated with or without SB203580 for 30 min, before addition of and further incubation with 2 μg/ml StxB for 20 min. The cells were then fixed and permeabilized before staining with the indicated antibodies. DRAQ5 was used for nuclear staining. Bar, 10 μm. Colocalization of StxB with the Golgi marker Giantin was quantified using Zeiss LSM Image Browser. Bars represent SD; n = 10. (c) We analyzed 1/100 of the Stx-IP supernatant (from D) for p38α by Western blot. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. (d) As in a, but in this case cells were transfected with 100 nM of the indicated siRNA and incubated for 48 h before StxB-Sulf2 treatment. These experiments were repeated at least three times with duplicates. (e) Cells were incubated for 20 min with 2 μg/ml Stx and 2 μg/ml ricin before fixation and permeabilization. They were then stained with antibodies as indicated. Bar, 10 μm. (f) As in d, but with 90-min incubation of ricin sulf-1 instead of StxB-Sulf2.