Figure 3.
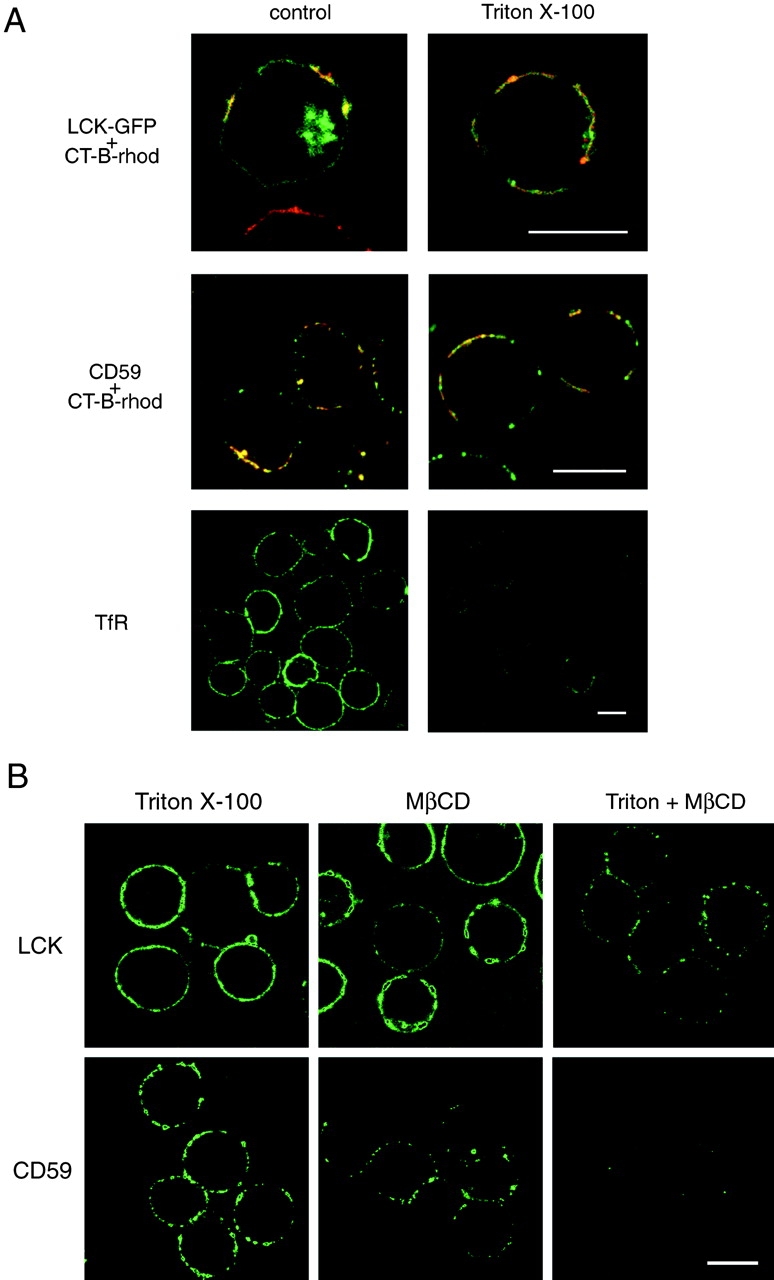
A, Detergent-resistance of proteins associated with CT-B patches. Jurkat cells transfected with LCK-GFP (top row) or left untransfected (other rows) were patched with CT-B–rhodamine plus anti–CT-B. They were then either directly fixed (control) or extracted with 1% Triton X-100 for 5 min on ice before fixation, as indicated. Untransfected cells were stained for CD59 or CD45, using FITC-conjugated secondary antibodies. Fluorescence of GFP and fluorescein (green) or rhodamine (red) was visualized by confocal microscopy, with identical settings for control versus treated samples. For images showing LCK and CD59 localization, red and green images were overlaid to reveal regions of colocalization (appearing yellow) with CT-B. Bars, 10 μm. B, Disruption of detergent-insoluble CT-B–patched proteins by MβCD. Jurkat cells were patched with CT-B/anti–CT-B and then treated with either 1% Triton X-100 for 10 min on ice, 10 mM MβCD for 15 min at 37°C, or MβCD followed by Triton X-100 extraction. The cells were then fixed and stained for LCK or CD59. Confocal images of the various treatments were taken with identical settings to allow comparison of staining. Bar, 10 μm.
