Figure 3.
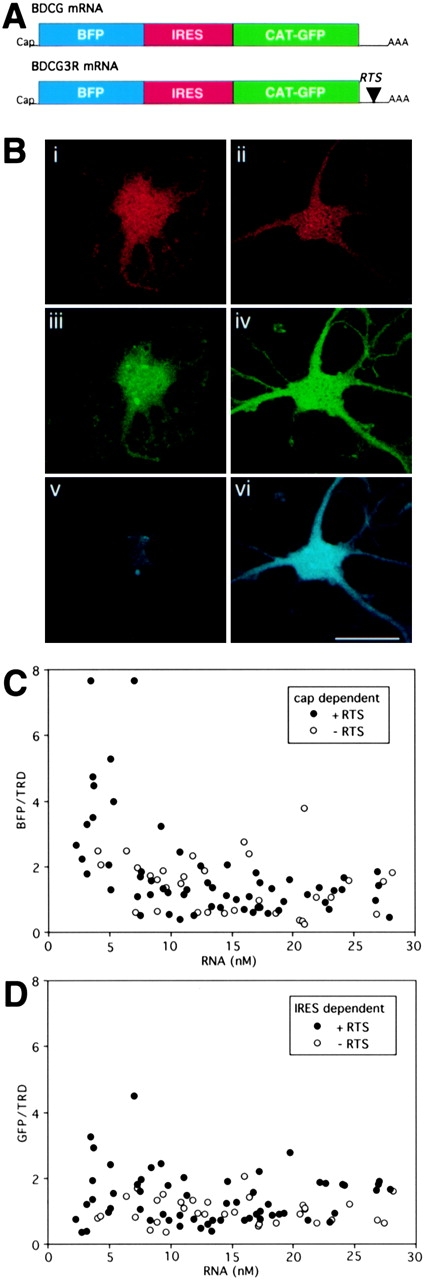
Ratiometric translation assay for discistronic RNA. (A) Structures of dicistronic RNAs. Dicistronic mRNAs encoding BFP in a cap-dependent cistron and GFP in an IRES-dependent cistron are shown. The RTS was inserted into the 3′UTR of the dicistronic RNA. (B) Triple channel confocal microscopy of oligodendrocytes injected with TRD and dicistronic RNA. Oligodendrocytes were microinjected with TRD and either nonRTS (left panels) or RTS-containing dicistronic RNA. After 24 h, the cells were analyzed by triple channel confocal microscopy. A representative cell is shown for each RNA. The TRD channel is shown in red (i and ii), the GFP channel in green (iii and iv), and the BFP channel in blue (v and vi). (C) Cap-dependent translation efficiency. B104 cells were microinjected with dicistronic RNA and imaged as described in B. For each triple channel image the pixel values in the three channels were integrated over the nucleus. The red channel provides a measure of injected TRD volume which is used to calculate intracellular RNA concentration. The blue channel provides a measure of expression of BFP. The ratio of BFP intensity to TRD intensity provides a measure of cap-dependent translation efficiency in each cell. Open circles indicate cells injected with nonRTS RNA. Closed circles indicate cells injected with RTS RNA. (D) IRES-dependent translation efficiency. B104 cells were microinjected with dicistronic RNA and imaged as described in B. For each triple channel image the pixel values in the three channels were integrated over the nucleus. The red channel provides a measure of injected TRD volume which is used to calculate intracellular RNA concentration. The green channel provides a measure of expression of GFP. The ratio of GFP intensity to TRD intensity provides a measure of IRES-dependent translation efficiency in each cell. Open circles indicate cells injected with nonRTS RNA. Closed circles indicate cells injected with RTS RNA.
