Figure 5.
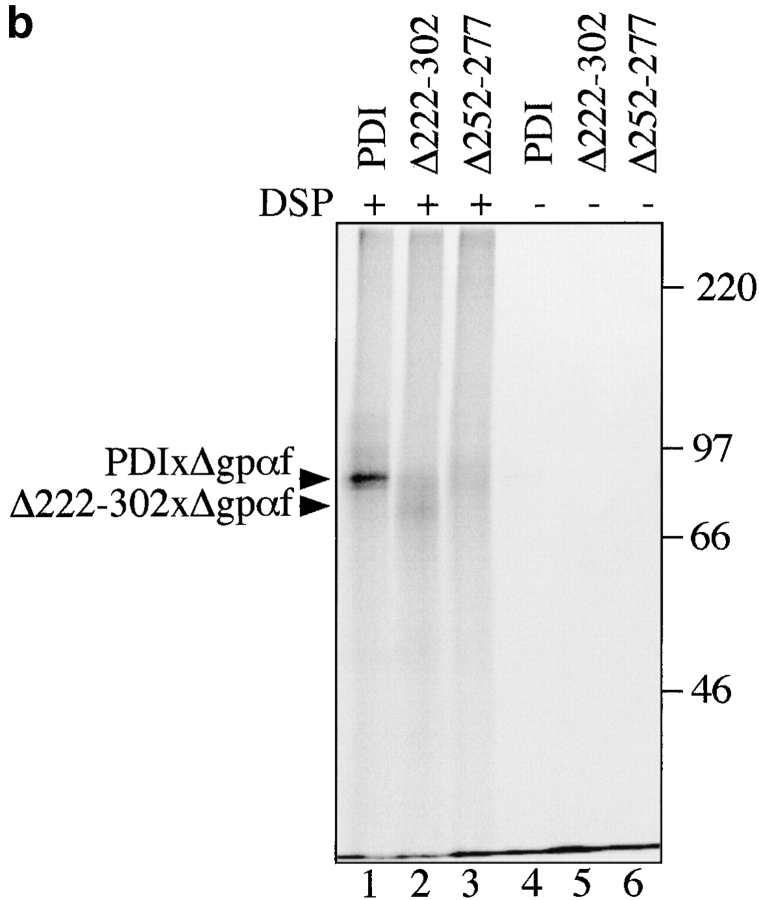
PDI specifically interacts with a misfolded, cysteine-free secretory protein. a, Wild-type PDI preferentially binds to Δgpαf. Radiolabeled pΔgpaf (lanes 1–3) or ppαf (lanes 4 and 5) were translocated into wild-type microsomes. Directly after termination of the translocation reaction, DSP cross-linking was performed as described in Materials and Methods, followed by solubilization of the membranes, and precipitation of glycoproteins with ConA-Sepharose or immunoprecipitation with anti-PDI antiserum. Cross-linked proteins were resolved on nonreducing 7.5% SDS gels and visualized by PhosphorImaging. The positions of major cross-linking products are indicated (PDIxΔgpαf and PDIxgpαf). Note that wild-type gpαf is a glycoprotein, thus, both monomeric gpαf (•, lanes 4 and 5) and gpαf dimers (*, lane 5) bind to ConA-Sepharose, whereas Δgpαf contains no oligosaccharyl side chains and, therefore, only binds to ConA-Sepharose if cross-linked to the glycoprotein PDI (lane 2). b, Radiolabeled pΔgpαf was translocated into wild-type and pdi1 mutant microsomes and cross-linked with DSP as described. Cross-linking products of Δgpαf and wild-type or mutant PDI proteins were detected by precipitation with ConA-Sepharose.