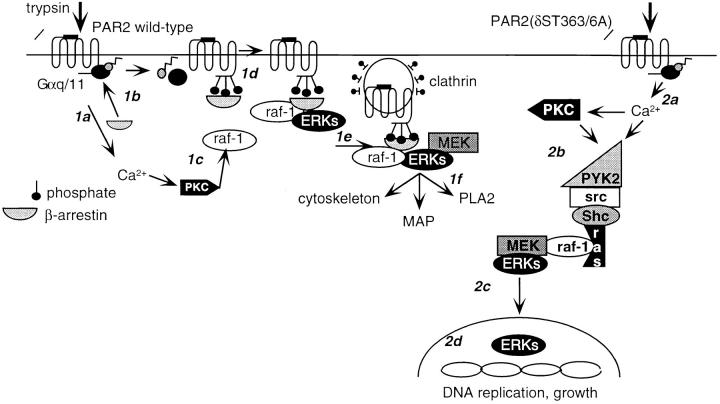
Figure 10.
Model for β-arrestin–dependent and –independent activation of ERK1/2 by PAR2. (1a) Trypsin cleavage and activation of wild-type PAR2 leads to transient Ca2+ mobilization and activation of PKC. (1b) PKC phosphorylates and activates raf-1. (1c) PAR2 binds β-arrestin and desensitizes. (1d) Raf-1 and ERK1/2 associate with β-arrestin–bound receptor and (1e) the complex associates with the clathrin-coated pit and ERK becomes activated. (1f) Cytosolic, active ERK1/2 phosphorylate cytoskeletal proteins, microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs), and phospholipase A2 (PLA2). (2a) Trypsin cleavage and activation of PAR2(δST363/6A) leads to sustained Ca2+ mobilization and transactivation of EGFR. (2b) Tyrosine phosphorylation of kinases such as PYK2 occur, activating the classic ras-dependent ERK1/2 pathway. (2c) ERK1/2 translocate to the nucleus. (2d) ERK1/2 phosphorylate and activate nuclear proteins, leading to DNA replication and cell growth.