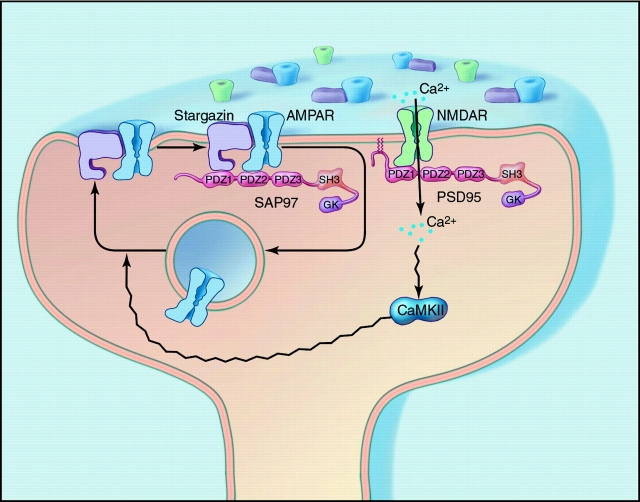
Figure 1.
Differential regulation of synaptic glutamate receptors by PDZ proteins. NH2-terminal palmitoylation anchors PSD-95 at the postsynaptic density, and PDZ domains from PSD-95 associate with the COOH termini of NMDA receptor subunits. By contrast, AMPA receptor delivery to the plasma membrane requires stargazin. Synaptic targeting of AMPA receptors requires stargazin binding to PDZ proteins such as SAP-97, which additionally binds the COOH terminus of the GluR1 subunit of AMPA receptors. Whereas NMDA receptors are firmly anchored at the postsynaptic membrane, synaptic expression of AMPA receptors is dynamically regulated by neuronal activity. During intense synaptic stimulation, calcium influx through NMDA receptors activates CaMKII, which mediates insertion of synaptic AMPA receptors.