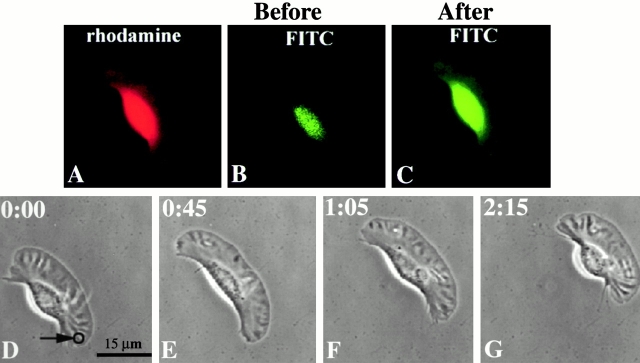
Figure 4.
Control experiment: photoactivation of caged FITC-dextran in the wing of the keratocyte. (A) Positive rhodamine fluorescence identifies a loaded cell. (B) Before uncaging, the fluorescence in the FITC channel was negligible, as expected. (C) After photoactivation, caged FITC-dextran was uncaged successfully as demonstrated by FITC fluorescence throughout the cell. (D–G) Time-lapse microscopy of the same cell shows unaltered locomotion as a result of such photorelease (the 3-μm zone of photoactivation is indicated by a circle).