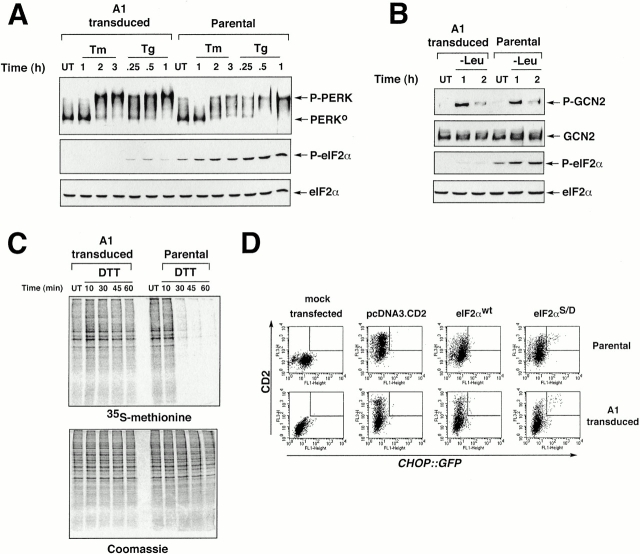
Figure 3.
The A1 GSE interferes with eIF2α phosphorylation and downstream signaling but does not block stress-activation of the eIF2α kinases PERK and GCN2. (A) Immunoblot of PERK immunoprecipitated from parental and A1-transduced cells after treatment with tunicamycin (2 μg/ml, Tm) or thapsigargin (100 nM, Tg) (upper panel). The positions of the higher mobility, inactive form of the protein (PERK0) and the lower mobility, phosphorylated active form of the protein (P-PERK) are indicated. Immunoblot of the same lysate with antisera that detects eIF2α phosphorylated on serine 51 (P-eIF2α), or total eIF2α. (B) Immunoblot of GCN2 immunoprecipitated from parental and A1-transduced cells cultured in leucine-deficient media where indicated (−Leu). GCN2 is revealed by immunoblot with an antiserum that detects the phosphorylated, active form of the kinase (P-GCN2), or an antiserum that reacts with all forms of the kinase (GCN2) (upper panels). Immunoblot of the same lysates with antisera to eIF2α as in A (lower panels). (C) Autoradiography of a SDS-PAGE gel of whole cell lysates from parental and A1-transduced CHO cells that had been treated with DTT (2 mM) for the indicated period of time to rapidly induce ER stress, and that had been pulsed with [35S]methionine. The lower panel shows a Coomassie blue stain of the same gel to control for equal loading of the lanes. (D) FACS® analysis of GFP activity in A1-transduced or parental CHOP::GFP CHO cells mock-transfected or transfected with expression plasmids that encode the CD2 cell surface marker alone, CD2 and wild-type eIF2α (eIF2αWT), or CD2 and S51D mutant eIF2α (eIF2αS51D). Note the population of double positive (CD2+ and GFP+) cells present only in the pool transfected with the mutant eIF2α (rectangle).