Figure 5.
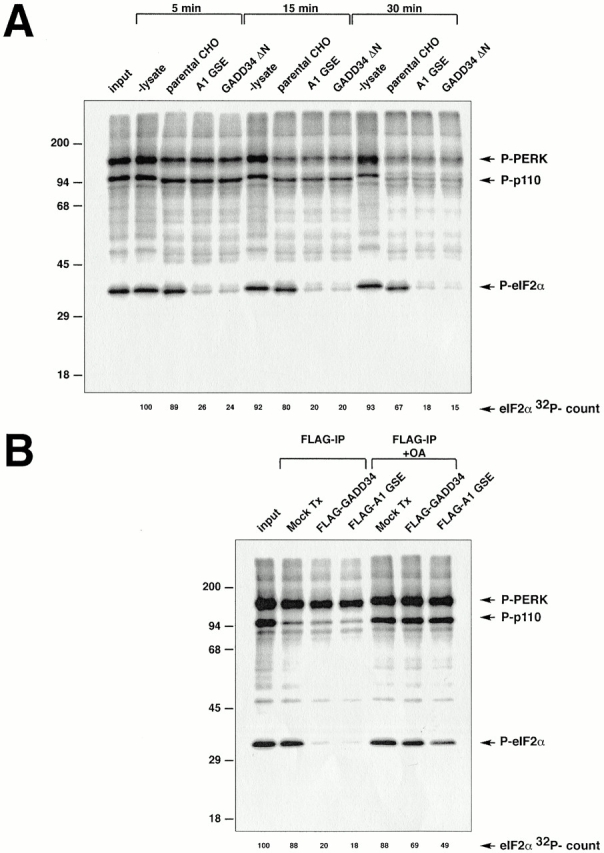
Cells expressing GADD34 have increased phosphatase activity directed towards eIF2α. (A) Autoradiogram revealing the in vitro dephosphorylation of radiolabeled eIF2α by lysates of cells expressing the A1 GSE or the mouse GADD34 COOH-terminal fragment (GADD34 ΔN). eIF2α in rabbit reticulocyte lysate was radiolabeled in vitro on serine 51 with GST-PERK, and incubated for the specified time with lysates of CHO cells expressing the indicated GADD34 derivatives. The position on the SDS-PAGE of radiolabeled eIF2α (P-eIF2α), GST-PERK (P-PERK), and an unidentified phosphoprotein of 110 kD present in the reticulocyte lysate (P-p110) are indicated. The latter two serve as controls for the specificity of the activity that dephosphorylates eIF2α. The radioactive signal associated with eIF2α is quantified in arbitrary units (eIF2α 32P-count). (B) Autoradiogram revealing the in vitro dephosphorylation of radiolabeled eIF2α by complexes immunoprecipitated from 293T cells transfected with epitope-tagged, full-length mouse GADD34 (FLAG-GADD34) or the A1 GSE (FLAG-A1 GSE), or mock-transfected cells (Mock Tx). The in vitro dephosphorylation assays were carried out in the absence or presence of phosphatase inhibitor (2 μM okadaic acid, +OA).
