Figure 3.
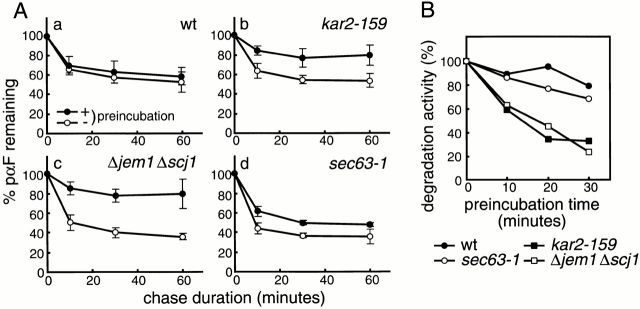
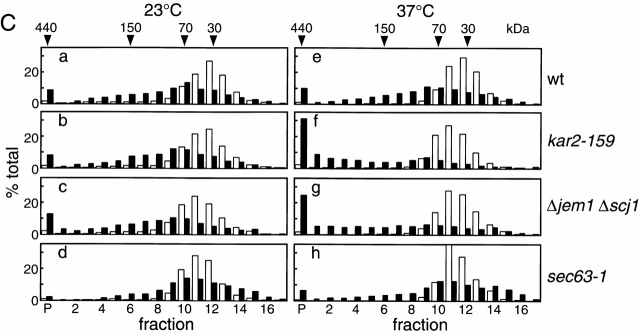
ERAD defects correlate with aggregation of ΔGpαF. (A) Radiolabeled ΔGppαF was translocated into microsomes prepared from wild-type (a), kar2-159 (b), Δjem1 Δscj1 (c), or sec63-1 (d) strains. After translocation, membranes were incubated on ice (○) or at 37°C (•) for 20 min in the presence of ATP. Cytosol prepared from the wild-type strain was added to a final concentration of 5 mg protein/ml, and posttranslocation chase reactions were performed at 37°C for the indicated times. Proteins were precipitated with trichloroacetic acid and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Relative amounts of ΔGpαF were quantified by radioimaging. Error bars indicate standard deviation from the means of at least four independent experiments. The amount of ΔGpαF at 0 min chase was set to 100%. (B) Radiolabeled ΔGppαF was translocated into microsomes prepared from wild-type (•), kar2-159 (▪), Δjem1 Δscj1 (□), or sec63-1 (○) strains. Membranes were recovered and incubated at 37°C in the presence of ATP for the indicated times. Cytosol was added to a final concentration of 5 mg protein/ml, and posttranslocation chase reactions were performed at 37°C for 20 min. Degradation activity was represented as the amount of ΔGpαF degraded, and the amount of ΔGpαF with 0 min preincubation was set to 100%. (C) Radiolabeled ΔGppαF and ppαF were translocated into microsomes prepared from wild-type (a and e), kar2-159 (b and f), Δjem1 Δscj1 (c and g), or sec63-1 (d and h) strains. After translocation, membranes were incubated at 23°C (a–d) or 37°C (e–h) for 20 min in the presence of ATP. Membranes were solubilized with 1% Triton X-100, subjected to sucrose density gradient centrifugation, and analyzed as in the legend to Fig. 2. Relative amounts of ΔGpαF and glycosylated pαF were quantified by radioimaging. Black bars, ΔGpαF; white bars, glycosylated pαF.