Figure 5.
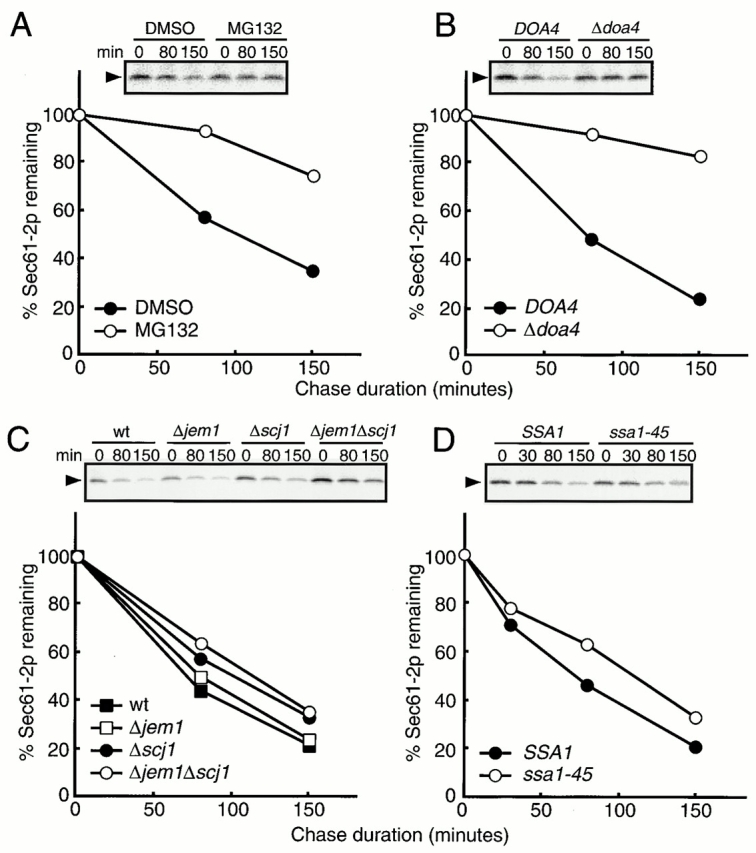
Jem1p and Scj1p are dispensable for the degradation of Sec61-2p. (A) Δerg6 cells with the sec61-2 background (SNY1081) were pulse labeled with 35S–amino acids for 10 min, and chased for the times indicated above the lanes at 38°C in the presence (MG132) or the absence (DMSO) of 200 μM MG132. Sec61-2p was recovered from cell extracts by immunoprecipitation using an anti-Sec61p antiserum and analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Relative amounts of Sec61-2p were quantified by radioimaging and the means of two independent experiments are shown. The amount of Sec61-2p at 0 min chase was set to 100%. •, pulse–chase experiment in the absence of MG132; ○, pulse–chase experiments in the presence of 200 μM MG132. (B) Δdoa4 (SNY1082) and its isogenic wild-type (DOA4, RDM15-5B) with the sec61-2 background were pulse labeled with 35S–amino acids for 10 min, chased for the times indicated above the lanes at 38°C, and analyzed as in A. The means of four independent experiments are shown. The amount of Sec61-2p at 0 min chase was set to 100%. •, wild-type; ○, Δdoa4. (C) Wild-type (RDM15-5B), Δjem1 (KYSC11), Δscj1 (SNY1070), and Δjem1 Δscj1 (SNY1071) cells with the sec61-2 background were pulse labeled with 35S–amino acids for 10 min, chased for the times indicated above the lanes at 38°C, and analyzed as in A. The means of two independent experiments are shown. The amount of Sec61-2p at 0 min chase was set to 100%. ▪, wild-type; □, Δjem1; •, Δscj1; ○, Δjem1 Δscj11. (D) ssa1-45 (SNY1078) and its isogenic wild-type (SSA1, SNY1077) strains with the sec61-2 background were pulse labeled with 35S–amino acids for 10 min, chased for the times indicated above the lanes at 37°C, and analyzed as in A. The means of two independent experiments are shown. The amount of Sec61-2p at 0 min chase was set to 100%. •, wild-type; ○, ssa1-45.
