Figure 1.
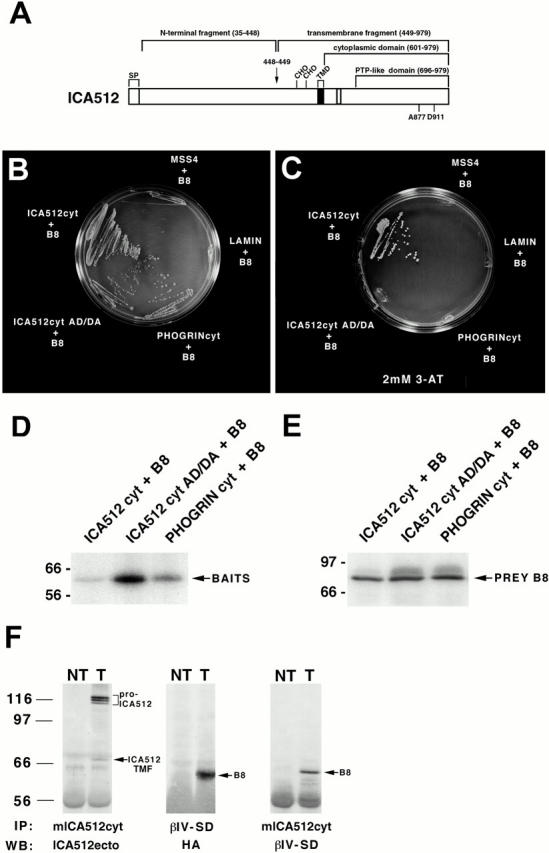
(A) Schematic representation of human ICA512. The protein includes 979 amino acids, including a signal peptide (SP), a single transmembrane domain (TMD), and a cytoplasmic domain with an inactive PTP domain. Cleavage at a consensus site for furin-like convertases between amino acids 448 and 449 (arrow) gives rise to an NH2-terminal fragment and a transmembrane fragment of 60–66 kD that includes the cytoplasmic domain. CHO, glycosylation sites. The residues in the PTP domain of ICA512 that distinguish it from active PTPs are indicated (A877, D911). (B–F) Interaction of the partial clone of βIV spectrin, B8, with ICA512cyt. (B and C) Yeast two-hybrid mating assay. L40 cells transformed with the prey plasmid pACTII-B8 were mated with AMR70 cells transformed with bait plasmids pLexA-ICA512cyt, pLexA-ICA512cyt AD/DA, pLexA-PHOGRINcyt, pLexA-lamin, or pLexA-MSS4 and grown on selective media in the absence (B) and presence (C) of 2 mM 3-AT. Cell survival reflects the interaction of the bait with the prey. (D and E) Expression levels of the different baits and B8 in L40-AMR70 mated cells as determined by Western blotting with an antiserum against LexA (D) and HA (E). (F) Coimmunoprecipitation of ICA512 and B8 from cotransfected COS cells. A mouse antibody directed against ICA512cyt or a rabbit antibody directed against the βIV spectrin specific domain (βIV-SD) were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) from Triton X-100 extracts of nontransfected (NT) and ICA512-B8 cotransfected (T) cells. Immunoprecipitates were Western blotted (WB) with affinity purified antibodies directed against the ectodomain of ICA512, βIV-SD, or a mouse antibody directed against HA. The arrows point to the immunoprecipitated ICA512 transmembrane fragment (ICA512 TMF) and B8, while a bracket indicates the position of pro-ICA512.
