Figure 1.
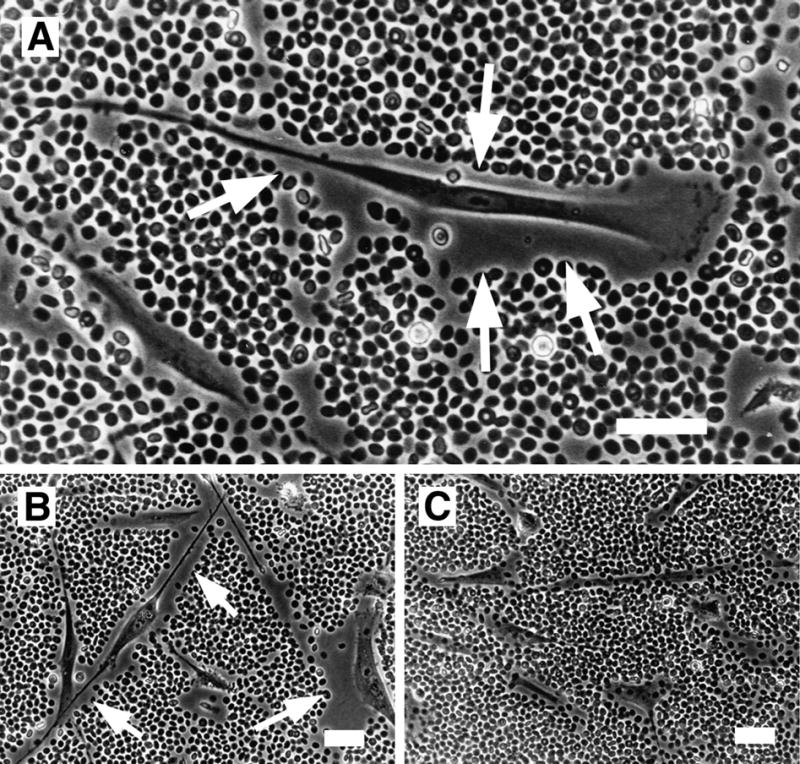
Hyaluronan-dependent pericellular matrix in human smooth muscle cells visualized using the particle exclusion assay. The cell coat excludes the fixed erythrocytes and is seen as a clear zone surrounding the cell (arrows). A. A typical locomoting cell with a small amount of pericellular matrix at the lammellipodium in front and more abundant matrix along the cell flanks and trailing uropod. B, C. Pericellular matrices were visualized before, B, or after, C, digestion with Streptomyces hyaluronidase. Bars equal 50 μm. Panel A originally published in: S. Evanko, J. Angello, T. Wight, Formation of hyaluronan and versican rich pericellular matrix is required for proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol., 1999, 19(4):1004–1013. Used with permission.
