Fig. 1. Generation of Tgfb1 knockin and Cre knockin mice.
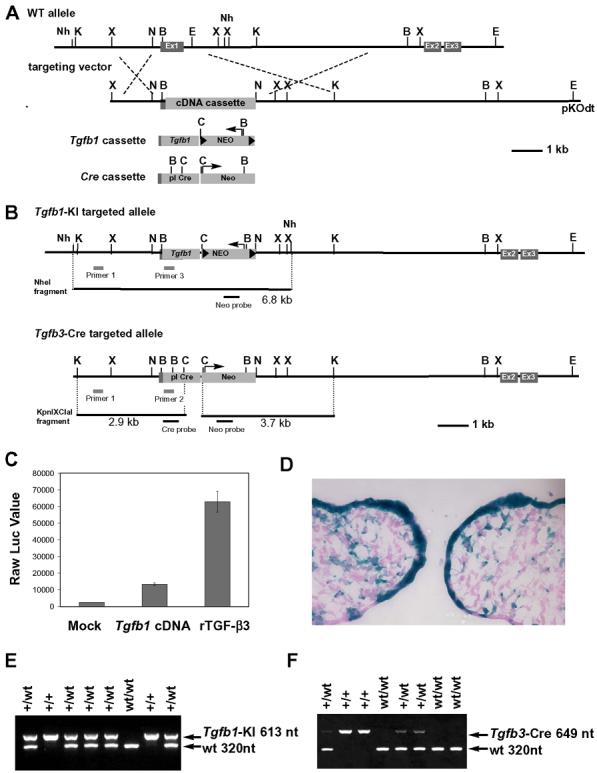
(A) A schematic diagram of Tgfb3 allele and targeting vectors for Tgfb1 knockin (Tgfb1-KI) and Cre knockin (Tgfb3-Cre). Ex1, Ex2, Ex3: Exon1, Exon2, and Exon3; Tgfb1 cassette: Tgfb1 cDNA with phosphoglycerate kinase polyA sequence and the pgk promoter driven neomycin-resistant gene flanked by loxP sites; Cre cassette: the promotorless Cre gene with the neomycin-resistant gene driven by the pgk promoter; Nh: NheI, K: KpnI, X: XhoI, B: BamHI, E: EcoRI, C: ClaI, N: NotI. (B) A schematic diagram for the targeted alleles. PCR and Southern blot screening strategies are illustrated. (C) Luciferase reporter assay for PCR-amplified Tgfb1 cDNA. MLE cells stably integrated with plasminogen activator inhibitor-1/luciferase reporter plasmid were cultured with supernatants from mock transfected cells (Mock) or Tgfb1 cDNA expression plasmid-transfected cells (Tgfb1 cDNA). The supernatant containing recombinant TGF-β3 at 10 ng/ml served as a positive control (rTGF-β3). Data are presented as raw luciferase values against each supernatant, n=2. (D) A lineage tracing assay for Tgfb3 expressing cells in the prefusion palate at E14: X-gal staining of the frontal frozen section from Tgfbr3-Cre+/−;R26R+/− embryos. (E-F) Genotyping of Tgfb1-KI and Tgfb3-Cre mice using PCR analysis.
