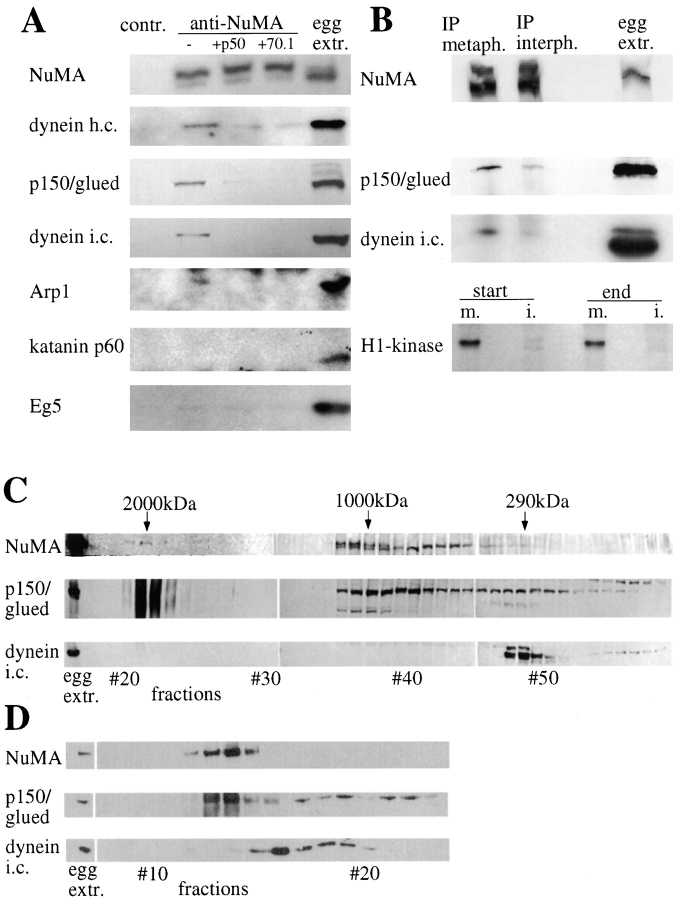
Figure 3.
A complex of NuMA, dynactin, and dynein is present in metaphase egg extracts. A, Immunoprecipitation experiments using a rabbit antibody against a COOH-terminal region of the Xenopus NuMA tail, or a control preimmune serum. Regular precipitations are shown in the first two columns, the following columns show experiments to which inhibiting amounts of dynamitin or antidynein intermediate chain mAb 70.1 were added. The last column displays immunoblots of 1 μl amounts of Xenopus egg extract. In the different rows, immunoblots are shown of Xenopus NuMA, cytoplasmic dynein heavy chain, dynactin p150/glued, cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain, dynactin Arp1α, katanin p60, and Eg5. Dark bands appearing at the top of the Arp1 immunoblot and at the bottom of the katanin immunoblot represent staining of the precipitating rabbit IgG at ∼50 kD by 125I-protein A. B, The coimmunoprecipitation of dynactin and dynein is mitosis-specific. Immunoblots of NuMA precipitations and frog egg extract aliquots were probed with antibodies against NuMA, dynactin p150/glued, and dynein intermediate chain. Metaphase-arrested extract and interphase extract were used for immunoprecipitations. Bottom, Autoradi-ography of phosphorylated histone H1 in mitotic (m.) and interphase (i.) extracts. Aliquots before and after completion of the immunoprecipitation were tested. C, Fractions of frog egg extract after a Sepharose 4B gel filtration column, tested by immunoblotting for NuMA, dynactin p150/glued, and dynein intermediate chain. Aliquots of extract before column chromatography are shown on the left. Molecular weight positions calculated from the calibration standards are indicated on the top. D, Column fractions from a Sephacryl S-400 gel filtration column of shorter size and shorter running time, immunoblotted for NuMA, dynactin p150/glued, and dynein intermediate chain.