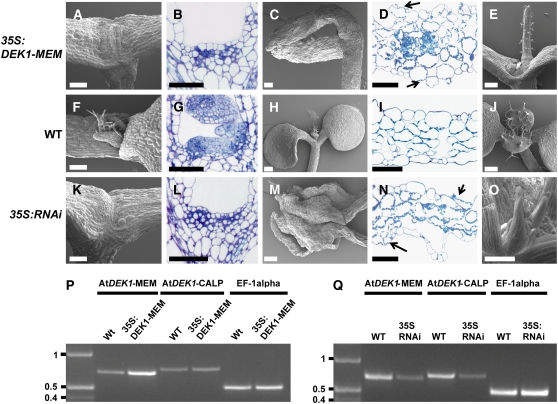
Figure 4.
Phenotypic Analysis of Arabidopsis Lines Expressing At DEK1-MEM and At DEK1-RNAi.
(A) to (E) Phenotypes of At DEK1-MEM seedlings.
(F) to (J) Comparable developmental stages and organs in wild-type seedlings.
(K) to (O) Comparable developmental stages and organs in At DEK1-RNAi seedlings.
The shoot apex is severely affected in At DEK1-MEM plants ([A] and [B]) and severely affected in RNAi lines ([K] and [L]). Cotyledons from At DEK1-MEM (C) and At DEK1-RNAi (M) seedlings are also distorted. Note in the cross sections of cotyledons from At DEK1-MEM (D) and At DEK1-RNAi (N) plants that the cells exposed to both adaxial and abaxial surfaces contain chloroplasts, suggesting that they have not completely differentiated into epidermal cells. Shoot apices from less severely affected seedlings in both At DEK1-MEM and At DEK1-RNAi lines can display one terminal radialized rosette leaf (E) or several radial rosette leaves (O). Bars = 100 μm.
(P) and (Q) RT-PCR analyses showing At DEK1 transcripts in At DEK1-MEM and wild-type seedlings (P) and in At DEK1-RNAi and wild-type seedlings (Q). The three primer sets used, specific for the At DEK1-MEM region, the At DEK1-CALP region, and EF-1α as a control to monitor template presence, are indicated at top. DNA marker sizes are indicated at left in kb.