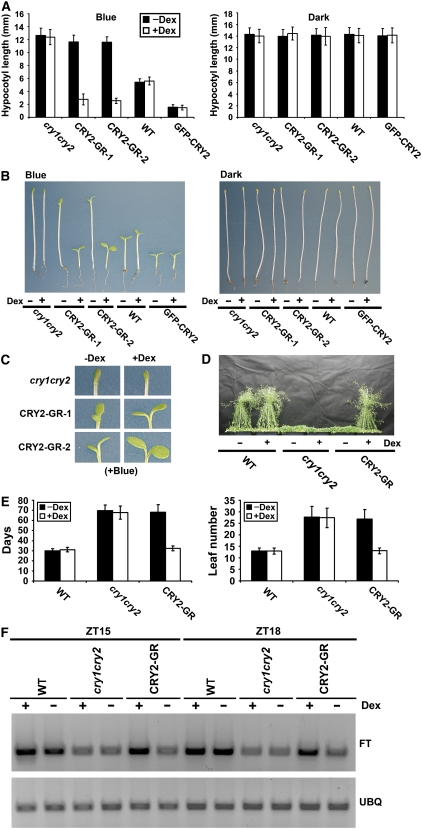
Figure 2.
Only Nuclear-Localized CRY2-GR Can Rescue the Long-Hypocotyl and Late-Flowering Phenotypes of the cry1 cry2 Mutant.
(A) Hypocotyl lengths of 5-d-old seedlings with indicated genotypes grown on soil watered with 30 μM Dex (+Dex) or mock solution (−Dex) in continuous blue light (16 μmol m−2 s−1) or in the dark. The means of hypocotyl lengths (n ≥ 20) and standard deviations of two independent lines (CRY2-GR-1 and CRY2-GR-2) are shown.
(B) Representative seedlings from samples shown in (A).
(C) A close-up cotyledon image of the seedling shown in the left panel of (B), with the indicated genotype and treatment shown.
(D) Representative 50-d-old plants of indicated genotypes (CRY2-GR/cry1 cry2 is line CRY2-GR-1). Plants were grown in long-day photoperiods (16 h light/8 h dark) and sprayed daily (from days 10 to 30) with 30 μM Dex (+Dex) or mock solution (−Dex).
(E) The flowering times of plants, for which the representatives are shown in (D). The flowering times are measured as days to flower (days) or number of rosette leaves (leaf number) at flowering, and the means and standard deviations (n ≥ 20) are shown.
(F) FT mRNA expression in the wild type, cry1 cry2, and CRY2-GR/cry1 cry2 (line CRY2-GR-1). Plants were grown on MS medium containing 30 μM Dex (+Dex) or mock solution (−Dex) in long-day photoperiods (16 h light/8 h dark). Samples were harvested at 15 (ZT15) and 18 (ZT18) h after light on, and the RT-PCR results are shown.