Figure 1.
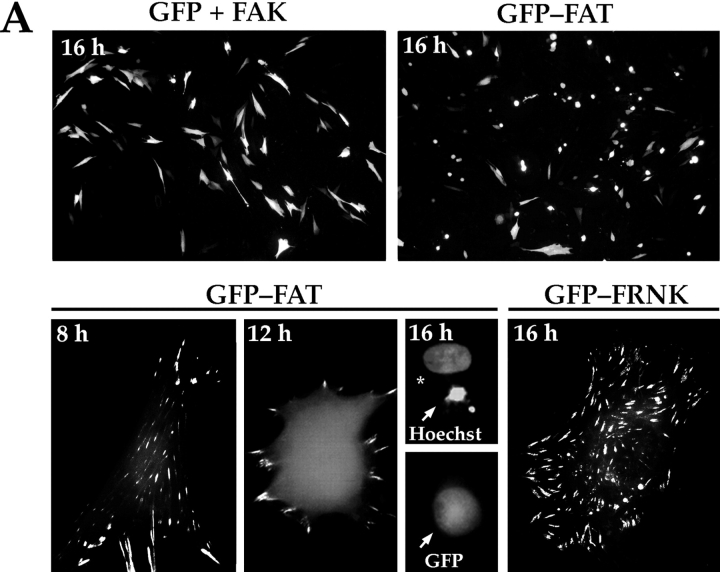
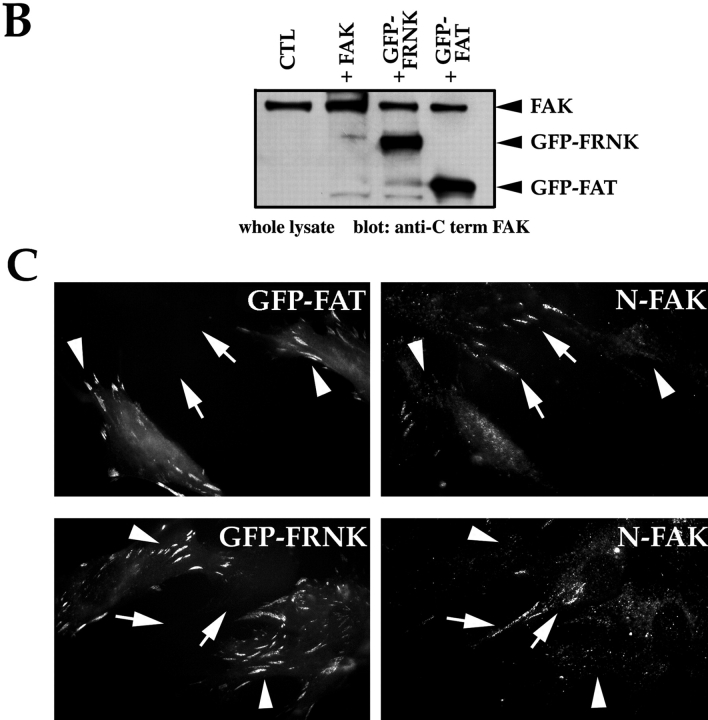
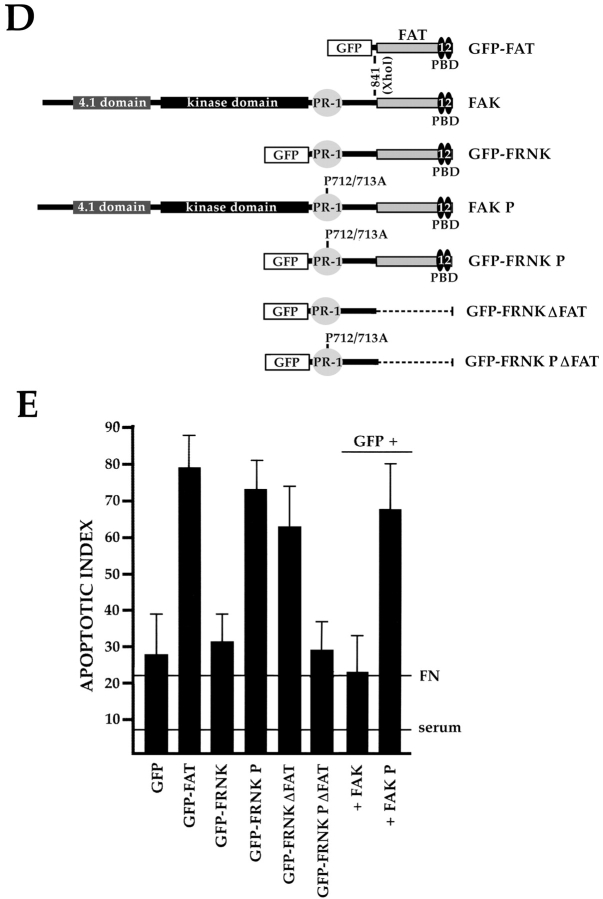
The PR-1 region of FAK/FRNK and focal contact localization are required for the transmission of FN matrix survival signals. RSF plated on FN in the presence of serum were transfected with wild-type FAK and GFP, GFP-FRNK, GFP-FAT, or GFP-FRNK with mutations in PR-1. Cells were cultured subsequently in the absence of serum for the times indicated. The apoptotic index was assessed by determining the percentage of transfected cells (GFP-positive) showing condensed or fragmented nuclei after staining with Hoechst dye. (A) Cells expressing GFP+FAK for 16 h remain spread on a FN matrix (upper left panel). Cells expressing GFP-FAT for 16 h (upper right panel) are rounded with condensed, fragmented nuclei. In cells expressing GFP-FAT for 8, 12, and 16 h (lower left panel), GFP-FAT initially localizes to focal contacts in spread cells. By 12 h, cells expressing GFP-FAT start to round. By 16 h, rounded cells have condensed nuclei as detected by Hoechst staining (arrow). Adjacent cell not expressing GFP-FAT has a normal nucleus (indicated by asterisk). In cells expressing GFP-FRNK for 16 h (lower right panel), GFP-FRNK localizes to focal contacts, but cells survive. (B) Expression levels of FAK, GFP-FRNK, and GFP-FAT in RSF 8 h after transfection. All are expressed at similar levels as shown by Western blot using a COOH-terminal FAK antibody. (C) GFP-FAT (upper row) and GFP-FRNK (lower row) both replace endogenous FAK in focal contacts. GFP, but not endogenous FAK, which is detected by an antibody against the NH2-terminal domain of FAK (N-FAK), is present in focal contacts of transfected cells (arrowheads). Nontransfected (GFP-negative) cells in the same field stain with N-FAK (arrows). (D) Diagrammatic representation of constructs used to test the importance of PR-1 in FAK and FRNK for supporting survival of RSF on a FN matrix (see text for description). (E) Apoptotic index for RSF transfected with constructs shown in D after 16 h. Mutation of PR-1 in both FRNK and FAK promotes apoptosis at levels comparable to GFP-FAT. A GFP-FRNK mutant that does not localize to focal contacts but has intact prolines 712–713 (GFP-FRNKΔFAT) is pro-apoptotic, whereas the GFP-FRNK P mutant that does not localize to focal contacts (GFP-FRNK PΔFAT) loses the ability to induce apoptosis. PBD, paxillin-binding domain.