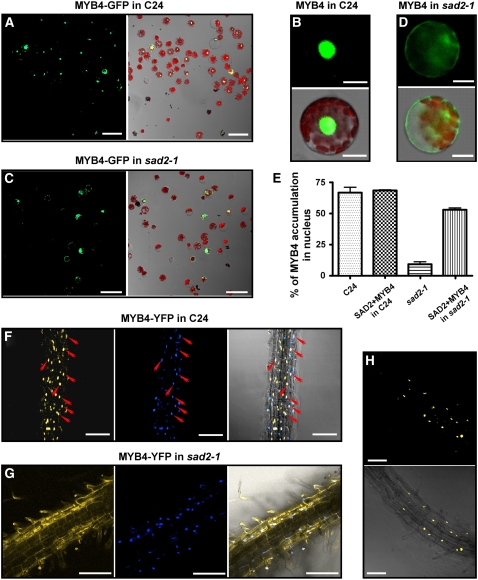
Figure 5.
SAD2 Is Required for MYB4 Nuclear Localization.
(A) to (E) Transient expression of MYB4-GFP in wild-type and sad2-1 protoplasts.
(A) and (C) MYB4-GFP nuclear localization in wild-type (A) or sad2-1 mutant (C) protoplasts. Left panels, confocal GFP images; right panels, combined bright-field, chloroplast autoflorescence, and GFP images.
(B) A protoplast showing typical nuclear-localized MYB4-GFP in the wild type.
(D) A protoplast showing typical cytoplasmic localized MYB4-GFP in the sad2-1 mutant. In (B) and (D), left panels are confocal GFP images, and right panels show combined bright-field, chloroplast autoflorescence, and GFP images.
(E) Effect of SAD2 on MYB4-GFP nuclear localization. 35SP:MYB4-GFP or 35SP:MYB4-GFP and 35SP:SAD2 were cotransfected into wild-type and sad2-1 protoplasts and the percentage of cells with nuclear-localized MYB4-GFP from each transformation was counted. Vertical bars represent se for three independent experiments.
(F) and (G) MYB4-YFP localized in the nucleus in the wild type (F) and in the cytoplasm in sad2 (G) transgenic plant roots (left panels), 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) nuclear staining (middle panels), and combined MYB4-YFP and DAPI staining (right panels). Arrows point to nuclei and show the colocalization of DAPI staining and the YFP signal (right panel in [F]).
(H) The sad2 MYB4-YFP transgenic plants were crossed to the wild type, and MYB4-YFP localization was determined in F1 heterozygous plants. MYB4 localized to the nucleus. Top panel, confocal GFP image; bottom panel, combined confocal and bright-field images.
Argon laser light (514-nm wavelength, 26% power) was used in (F) and (H); argon laser light (514-nm wavelength, 65.5% power) was used in (G). Bars in (A) and (C) = 50 μm, bars in (F) to (H) = 100 μm, and bars in (B) and (D) = 10 μm.