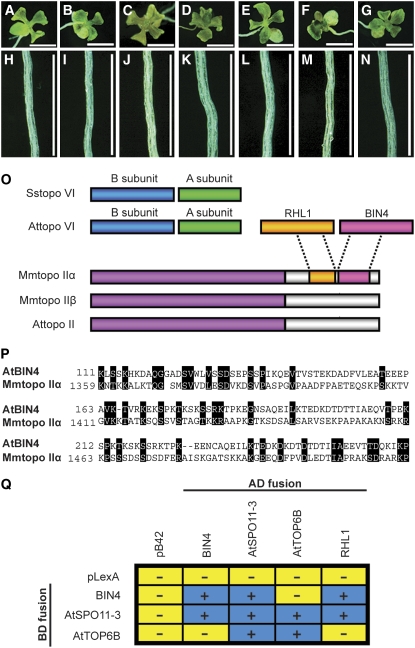
Figure 3.
Genetic and in Vivo Interactions between BIN4, RHL1/HYP7, At SPO11-3/RHL2/BIN5, and At TOP6B/RHL3/HYP6/BIN3.
(A) to (N) Ten-day-old, light-grown seedlings ([A] to [G]) and roots ([H] to [N]) of bin4-1 ([A] and [H]), hyp7 ([B] and [I]), hyp6 ([C] and [J]), rhl2 ([D] and [K]), bin4-1 hyp7 ([E] and [L]), bin4-1 hyp6 ([F] and [M]), and bin4-1 rhl2 ([G] and [N]). Bars = 2 mm in (A) to (G) and 0.5 mm in (H) to (N).
(O) Schematic representation of type II DNA topoisomerases from archaea, animals, and plants. Sstopo VI, topo VI from Sulfolobus shibatae; Attopo VI, topo VI from Arabidopsis; RHL1, RHL1 from Arabidopsis; BIN4, BIN4 from Arabidopsis; Mmtopo II, topo II from Mus musculus; Attopo II, topo II from Arabidopsis. RHL1/HYP7 and BIN4 exhibit partial sequence homology with the C-terminal domain of Mm topo IIα.
(P) Sequence alignment of the N-terminal domain of At BIN4 and the C-terminal domain of Mm topo IIα (GenBank accession number NP035753). Numbers refer to the amino acid length of each deduced protein, and black boxes represent similar or identical amino acids.
(Q) Yeast two-hybrid analysis of BIN4, RHL1/HYP7, At SPO11-3/RHL2/BIN5, and At TOP6B/RHL3/HYP6/BIN3 protein interactions. The BIN4, RHL1/HYP7, At SPO11-3/RHL2/BIN5, and At TOP6B/RHL3/HYP6/BIN3 genes were cloned into pLexA (BD, binding domain fusion) and pB42AD (AD, activator domain fusion) vectors, and their protein interactions were detected by induction (+, blue boxes) or no induction (−, yellow boxes) of the lacZ reporter gene.