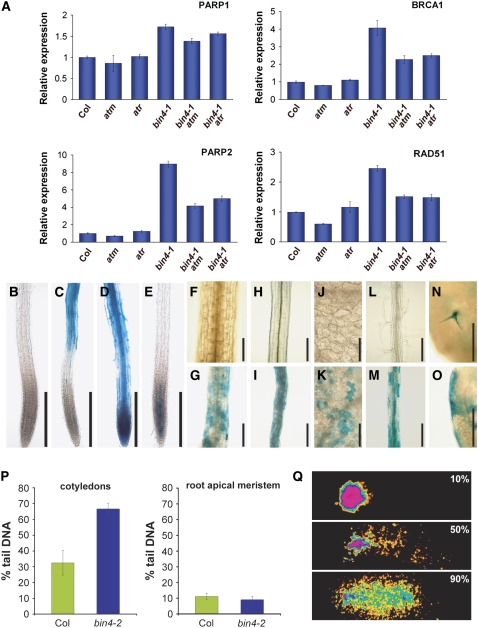
Figure 5.
The bin4 Mutation Triggers an ATM/ATR-Dependent DNA Damage Response in Postmitotic Cells.
(A) Quantitative real-time expression analysis of the DSB-inducible genes PARP1, PARP2, BRCA1, and RAD51 in 14-d-old wild-type, bin4-1, atm, atr, bin4-1 atm, and bin4-1 atr seedlings. The Actin2 expression level was used as a reference. The values represent averages of four independent replicates ± sd. Col, Columbia ecotype.
(B) to (E) pPARP2:GUS expression in wild-type primary roots (B), bin4-1 primary roots (C), wild-type primary roots exposed to 10 μg/mL bleomycin for 21 h (D), and wild-type primary roots exposed to 100 μM etoposide for 21 h (E).
(F) to (O) pPARP2:GUS expression in 7-d-old, light-grown hypocotyls ([F] and [G]), 4-d-old, dark-grown hypocotyls ([H] and [I]), mature cotyledons ([J] and [K]), mature roots ([L] and [M]), and mature leaves ([N] and [O]). (F), (H), (J), and (L) show wild-type organs, and (G), (I), (K), and (M) to (O) show bin4-1 organs.
(P) Statistical analysis of a comet assay comparing relative DNA damage in nuclei of 8-d-old wild-type and bin4-2 cotyledons (left panel) and root apical meristems (right panel). The means of 70 comets from five individual gels were assessed per sample. Error bars represent sd.
(Q) Examples of comets exhibiting 10% (top), 50% (middle), and 90% (bottom) tail DNA in comets.
Bars = 200 μm in (B) to (E) and (H) to (K), 100 μm in (F) and (G), and 250 μm in (L) to (O).