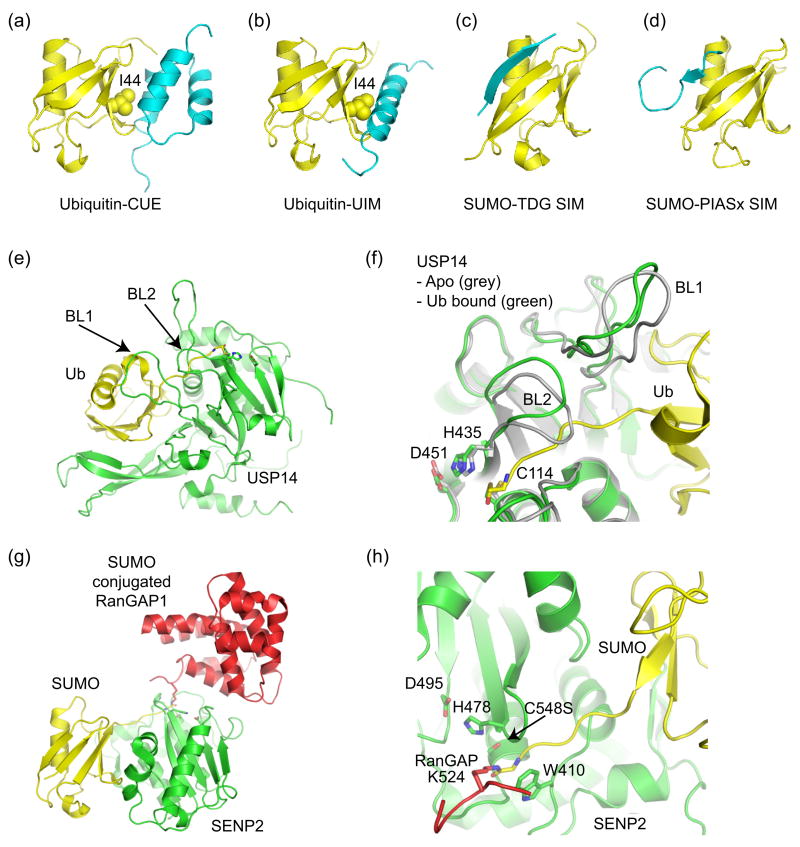
Figure 4.
Ub/Ubl binding domains and Ub/Ubl proteases. (a) Ub in complex with CUE (PDB code 1OTR, [36,37]). (b) Ub in complex with UIM (PDB code 1Q0W, [35]). CUE and UIM domains recognize the Ub hydrophobic patch centered about Ile44. (c) SIM from thymine DNA glycosylase (TDG) in complex with SUMO indicating an anti-parallel orientation for the SIM β-strand (PDB code 1WYW, [39]), similar to that observed for the Nup358 IR1 SIM domain (Figure 3c). (d) SIM from PIASx adopts a parallel β-strand orientation in complex with SUMO (PDB code 2ASQ, [40]). (e) Structure of Ub protease USP14 in complex with Ub-aldehyde (PDB code 2AYO, [43]). Blocking loops (BL1 and BL2) are denoted. (f) In Apo-USP14 (grey) (PDB code 2AYN), BL1 and BL2 occlude access to the preformed catalytic site. In USP14-Ub-aldehyde (green), Ub induces a conformational change wherein BL1 and BL2 move away to provide access to the catalytic site. Active site residues are shown. (g) Structure of SUMO protease SENP2 in complex with SUMO conjugated RanGAP (PDB code 2IO2, [47•]). (h) Close-up of the SENP2 active site to illustrate the 90° kink and isopeptide bond between RanGAP and SUMO. Similar structures were observed for SENP1 [48•]. Active site residues are shown.