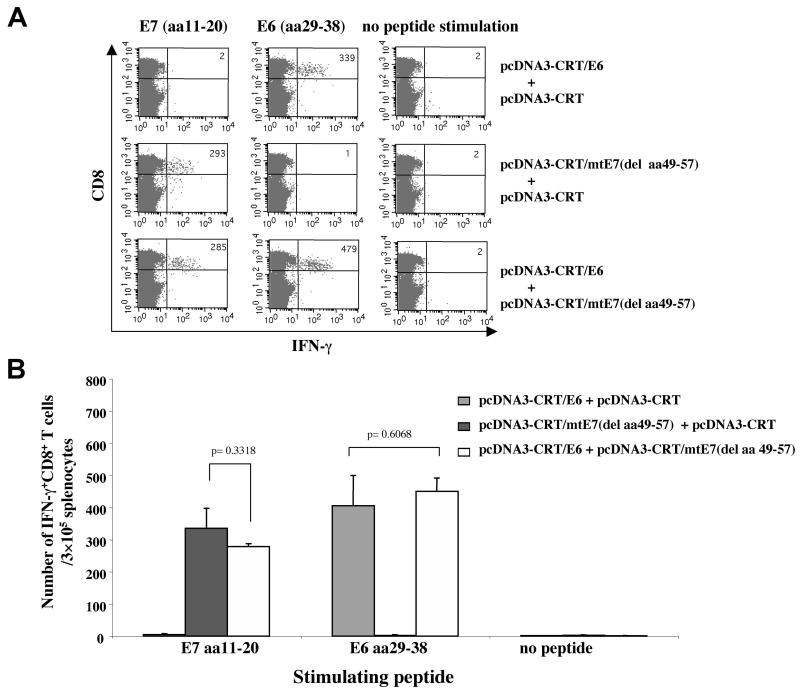
Figure 4. Intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry analysis of E6 or E7-specific IFN-γ-secreting CD8+ T cells in vaccinated HLA-A*0201mice.
HLA-A*0201 transgenic mice (AAD, on C57BL/6 background) (5 per group) were immunized and boosted intradermally via gene gun with the following vaccination groups: 1) pcDNA3-CRT/E6 (2μg/mouse, right side of the abdomen) and pcDNA3-CRT (2μg/mouse, left side of the abdomen), 2) pcDNA3-CRT/mtE7(del aa49-57) (2μg/mouse, right side of the abdomen) and pcDNA3-CRT (2μg/mouse, left side of the abdomen) or 3) pcDNA3-CRT/E6 (2μg/mouse, right side of the abdomen) and pcDNA3-CRT/mtE7(del aa49-57) (2μg/mouse, left side of the abdomen). Splenocytes from vaccinated mice were harvested one week after the last boost and stimulated with either E7 (aa11-20) or E6 (aa29-38) peptides. Splenocytes without peptide stimulation were used as a negative control. The cells were then stained for both CD8 and intracellular IFN-γ. (A) Representative figure of the flow cytometry data. (B) Bar graph depicting the number of antigen-specific IFN-gamma-secreting CD8+ T-cell precursors/3 × 105 splenocytes (mean±S.D.).