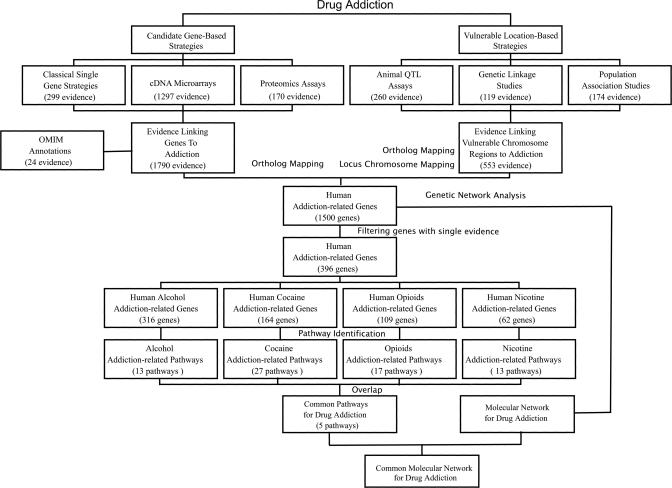
Figure 1. Pipeline for Collection of Data and Identification of (Common) Molecular Networks for Drug Addiction.
Strategies used to study the genetic and environmental influences underlying addiction were divided into two types. Candidate gene-based strategies identified a list of genes related to addiction, including candidate genes identified in classical animal models, significantly differentially expressed genes identified in microarray or proteomics assays, and OMIM annotations. Strategies focused on genetic factors identified a list of addiction-vulnerable regions through animal QTL studies, genetic linkage studies, and population association studies. We integrated these datasets and obtained a list of human addiction-related genes. This dataset was then divided into four subsets based on addictive drugs, and analyzed using KOBAS, a statistical method to identify enriched molecular pathways. Molecular pathways enriched for all subsets were considered to be common pathways for drug addiction, which were further connected to construct a common molecular network underlying different types of addiction.