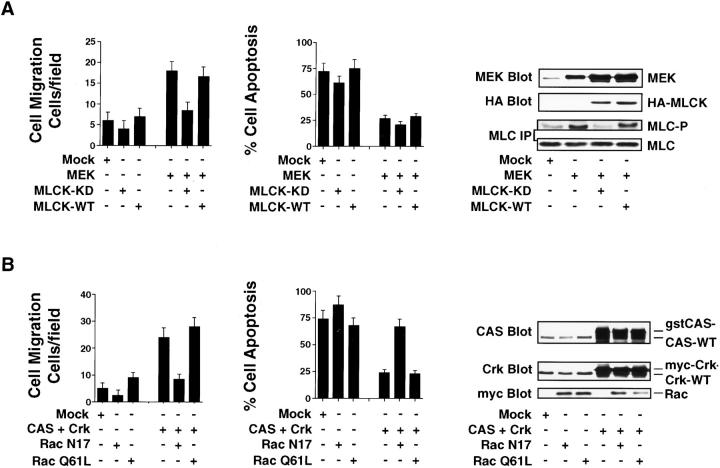
Figure 9.
CAS/Crk-mediated cell invasion and suppression of apoptosis requires Rac activity, whereas ERK-induced invasion, but not survival, requires MLCK activity. (A) COS-7 cells examined for cell migration and apoptosis in 3-D collagen after transfection with the empty vector (Mock), mutationally activated MEK alone, HA-tagged wild-type (WT), or kinase-dead (KD) MLCK and a β-gal reporter construct. The number of transfected migratory cells after 6 h or the percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by morphological criteria after 24 h of culture in 3-D collagen as described in Materials and Methods. Results are the mean ± SEM of three cultures from three independent experiments. Cells transfected as described above were lysed in detergent and Western blotted for MEK and HA. In some cases, MLC was immunoprecipitated from cells metabolically labeled with [32P]orthophosphate and examined for changes in phosphorylation and total MLC protein as described in Materials and Methods. (B) COS-7 cells examined for cell migration and apoptosis in 3-D collagen after transfection with the empty vector (Mock), CAS and Crk alone, myc-tagged mutationally inactivated (RacN17), or activated Rac (RacQ61L). Cells transfected as described above were evaluated for migration and apoptosis as described above. Results are the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Cells transfected as described above were lysed in detergent and Western blotted with myc, Crk, and CAS antibodies as indicated. CAS and Crk are glutathione S-transferase– and myc-tagged, respectively, and show reduced mobility in SDS-PAGE compared with endogenous forms of these proteins.