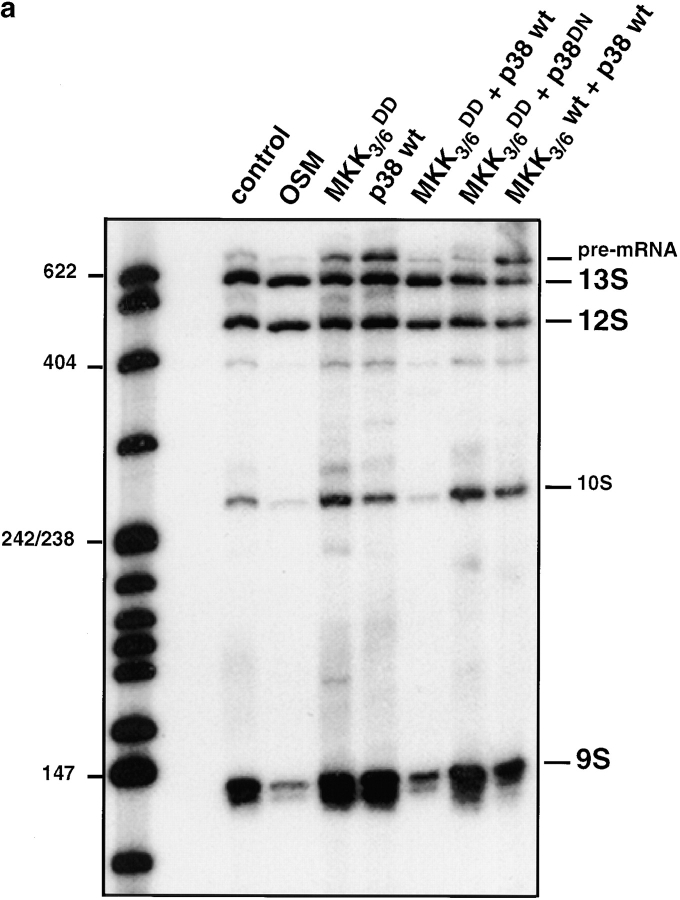
Figure 7.
Activation of the MKK3/6-p38 pathway and the concomitant reduction of the level of nuclear hnRNP A1 correlates with changes in alternative splicing. COS cells were transiently transfected with 6 μg of plasmid encoding the E1A splicing reporter minigene alone or together with 7 μg of expression plasmids encoding myc-tagged versions of the MKK3/6 kinase, or its permanently active mutant (MKK3/6 DD), in conjunction with 7 μg of expression plasmids encoding HA-tagged versions of wild-type p38 kinase or its dominant-negative mutant (p38DN). At 24 h after transfection cells were either left untreated or exposed to 600 mM sorbitol for 4 h. Total RNA was then isolated and the alternative splicing pattern of the E1A transcripts was determined by RT-PCR. The relative levels of 13S, 12S, and 9S mRNAs were quantitated as described (Cáceres et al. 1994; Screaton et al. 1995). The E1A transcript isoforms are shown schematically. Essentially identical results were obtained in three independent experiments.