Fig. 3.
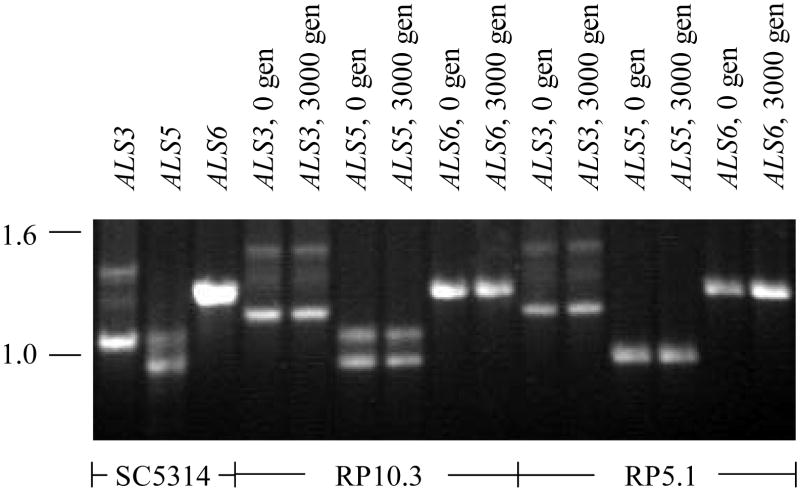
Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel of PCR products from amplification of the tandem repeat region of various ALS genes. Products from amplification of strain SC5314 genomic DNA are shown to demonstrate the PCR strategy illustrated in Fig. 1. Primers ALS3GenoF2 and ALS3GenoR2 were used to amplify the tandem repeat domain of ALS3, primers ALS5Geno2F and ALS5Geno2R for ALS5, and ALS6Geno2F with ALS6Geno3R for ALS6 (Table 1). The tandem repeat domain from each of these genes was also amplified from genomic DNA extracted from strains RP10.3 and RP5.1 grown for either zero or 3000 generations (labeled “0 gen” and “3000 gen”, respectively in the figure). Co-migration of the PCR products from the strains at generation 0 and 3000 suggests stability of the tandem repeat copy number in each gene over serial passage in vitro. A similar result was obtained from analysis of two other C. albicans strains grown for 3000 generations (RP39.1 and RP39.2) and with the second set of PCR genotyping primers for each ALS gene (data not shown). Molecular sizes (in kb) are shown to the left of the figure.