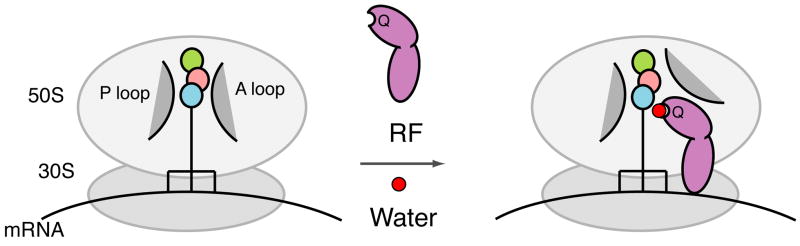
Figure 5. Model depicting two molecular contributions to release catalysis by RF1.
P-site bound tRNA carrying a tripeptide (colored circles) is protected in the absence of an A-site substrate by ribosomal RNA including the A and P loops (Schmeing et al., 2005b). RF1 (lavender) contributes to catalysis of peptide release by 1) “opening up” the ribosomal active site to allow solvent entry and 2) specific activation of a water molecule (red) controlled by the GGQ glutamine (Q).