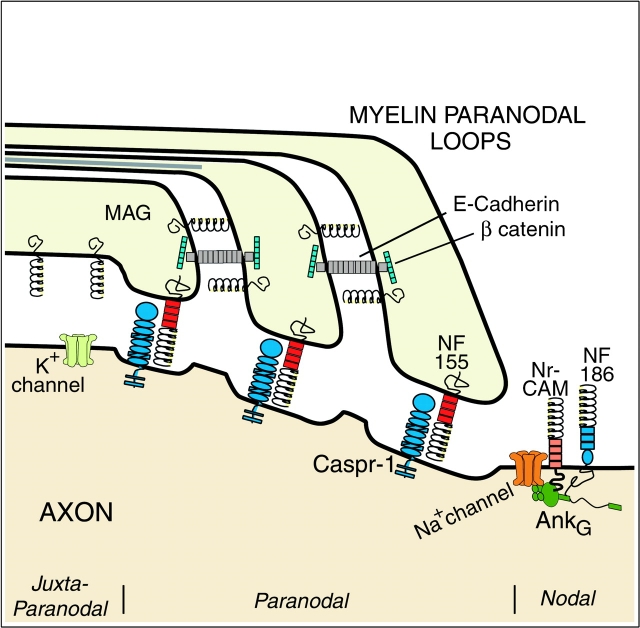
Figure 1.
A schematic of nodal region in longitudinal orientation. Three regions can be distinguished based on ultrastructure and molecular composition. The juxtaparanodal axon membrane contains high concentration of K+ channels. The adaxonal myelin membrane and paranodal loops (PNS only) contain MAG. The paranodal loops are connected to each other by adherens junctions that contain E-cadherin and β catenin and to the axon by septate-like junctions that contain caspr-1 and neurofascin 155. Na+ channels cluster in the nodal axolemma and bind to the skeletal protein ankyrinG. Neurofascin 186 and NrCAM also bind ankyrinG and may help target Na+ channels to the node.