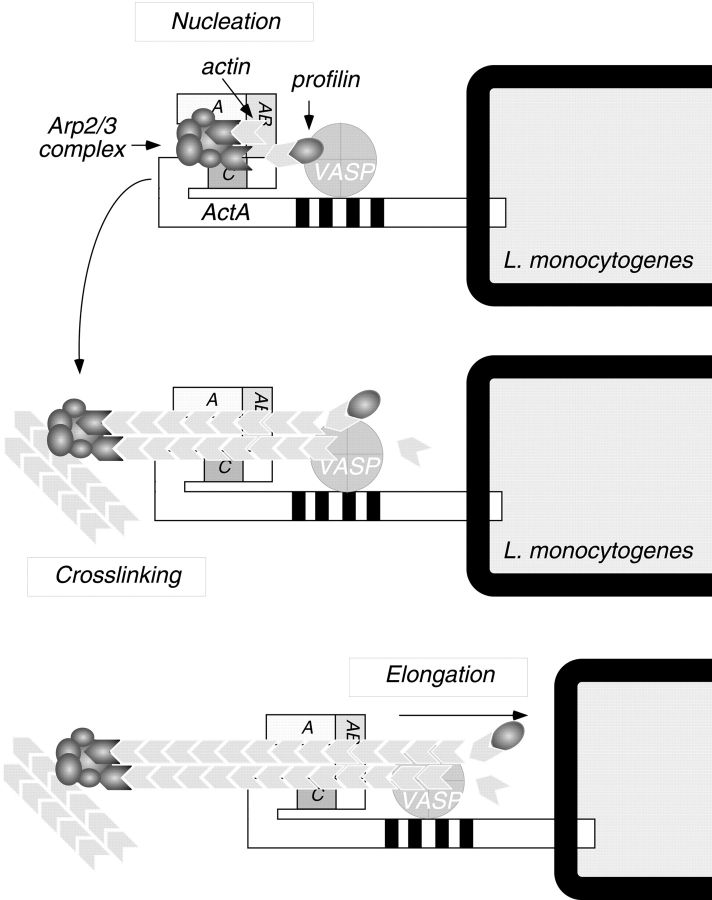
Figure 10.
Model for actin nucleation by ActA and the Arp2/3 complex at the L. monocytogenes surface. The NH2-terminal domain of ActA interacts directly with the Arp2/3 complex. The acidic stretch (A) and cofilin homology sequence (C) of ActA both contribute to Arp2/3 complex activation, whereas the actin-binding region (AB) recruits and presents the actin monomer to facilitate formation of an actin nucleus. After nucleation takes place, the Arp2/3 complex dissociates from ActA, and its cross-linking activity contributes to the structure of the comet tail. During bacterial motility, profilin may speed the rate of filament elongation by delivering actin monomers to the exposed barbed ends of nucleated filaments, and VASP may bind newly formed filaments to help maintain their association with the bacterial surface.