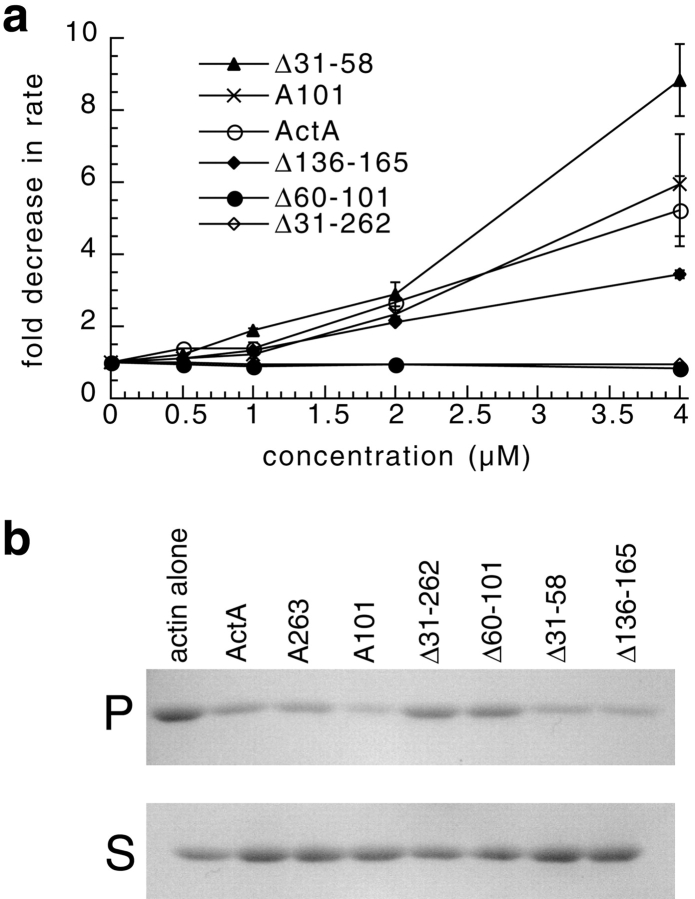
Figure 6.
High concentrations of ActA and a subset of ActA derivatives slow actin polymerization in the absence of the Arp2/3 complex. (a) Graph of the fold inhibition of the maximal rate of pyrene-actin polymerization versus the concentration of ActA or ActA derivatives. The pyrene-actin assay was carried out in the presence of 2 μM actin and the indicated concentrations of ActA derivatives. The fold inhibition was calculated by dividing the maximal rate of polymerization of actin alone by the maximal rate of polymerization in the presence of ActA (bars represent SEM). (b) An actin pelleting assay was used to assess the inhibitory effect of ActA and ActA derivatives on actin polymerization. 1 μM actin was polymerized for 10 min in the presence or absence of 5 μM ActA or ActA derivatives. Actin filaments (F-actin) were separated from monomers (G-actin) by centrifugation. The amount of F-actin in the pellet (P) and G-actin in the supernatant (S) fractions was visualized on a 12% polyacrylamide gel stained with Coomassie blue.