Figure 1.
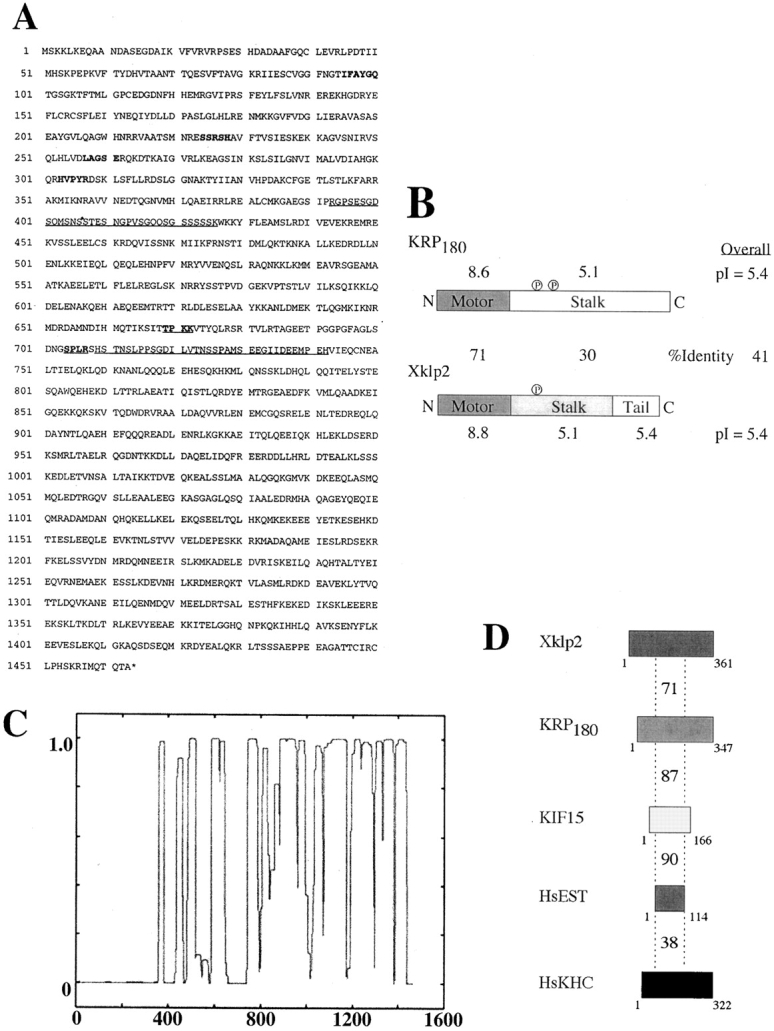
Molecular analysis of sea urchin KRP180. (A) The deduced amino acid sequence of KRP180 encodes an NH2-terminal motor polypeptide 1,463 amino acid residues long. Amino acids in bold correspond to the hyperconserved motor sequences found in kinesin motor domains. PEST sequences are shown as underscored amino acids. Underscored and bold amino acids correspond to consensus p34cdc2 kinase phosphorylation sites. The nucleotide sequence of KRP180 is available from GenBank under accession number AF28433. (B) Aligned linear maps of the motor polypeptides KRP180 and Xklp2 demonstrate the conservation of sequence identity and isoelectric point values in their domain organization. Consensus p34cdc2 kinase phosphorylation sites are shown as a circled letter P. Sequence identity scores are shown as percentages between the linear maps, isoelectric point values are shown above and below the linear maps, and overall scores are shown on the right. (C) KRP180 forms an extensive region of α-helical coiled-coil as determined in a Lupus plot using the Coils program (Lupus et al. 1991). (D) Linear maps of the full-length and partial motor domains of the Xklp2 members found in Xenopus (Xklp2), sea urchin (KRP180), mouse (KIF15), and human (HsEST), as well as the motor domain of human conventional kinesin heavy chain (HsKHC) demonstrate a region in the catalytic core of the motors, equal to the size of the smallest of the motors shown (HsEST), share identity to the Xklp2 motor domain. Identity scores compared with Xklp2 are shown above each motor domain.
