Figure 1.
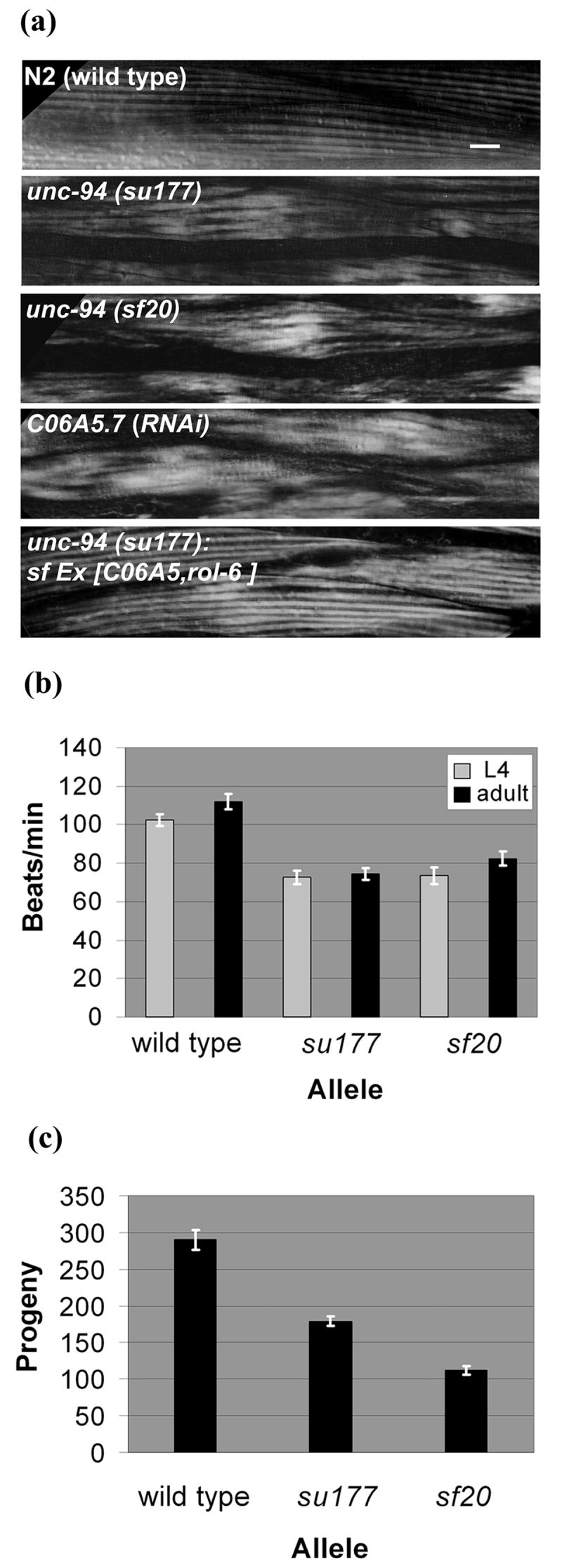
unc-94 mutants show disorganized muscle structure, decreased motility and low brood size. (a) Polarized light microscopy of body wall muscle in adult worms. In wild type muscle there is a normal arrangement of alternating birefringent A-bands with dark I-bands that run parallel to the long axis of the worm. In the muscle of worms expressing the two mutant alleles and C06A5.7 (RNAi) animals, there is reduced organization with alternation between normal and increased width of individual birefringent bands. The mutant phenotype can be rescued in unc-94 transgenic animals that carry an extrachromosomal array of the cosmid C06A5. Scale bar represents 10 μm. (b) Liquid motility assays of wild type and unc-94 animals at the 4th larval (L4) and adult stages of development. Data are shown as means and SEMs, with n=30. Both mutant alleles show reduced motility as compared to wild type. (c) Brood size assay comparing the amount of eggs laid by wild type animals and the unc-94 mutants. As shown, a normal N2 animal can lay between 200-300 eggs. Both unc-94 mutants show a significant decrease in their brood sizes, with su177 laying about 40% fewer eggs and sf20 laying 60% fewer eggs than wild type animals.
