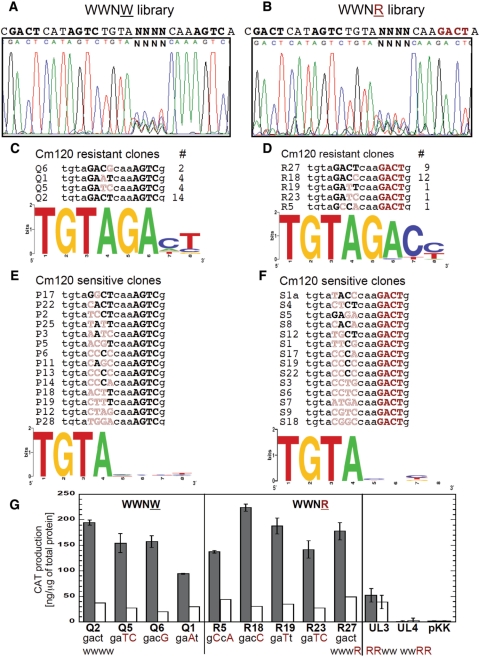
Figure 5.
Randomized C-half-box 2A libraries and selected variants. (A) Sequencing trace of the pooled randomized C-half-box 2A plasmid library before selection. All other C-half-boxes were WT (WWNW, where ‘N’ indicates the randomization), and the promoter region library is upstream of a promoterless cat gene. (B) Sequencing trace as in (A), except that in this library C-half-box 2B is replaced by the reversed complement (AGTC→GACT; WWNR). (C) The selection for C.PvuII-activated variants was as described in Figure 4B. The resulting sequences from the WWNW library, number of variants showing each recovered sequence, and Logo analysis are shown. (D) Sequences that could be activated detectably as in (C), but for the WWNR library. (E) The isolation of variants that are not detectably activated by C.PvuII was as described in Figure 4C. The resulting sequences from the WWNW library and Logo analysis are shown. (F) Sequences that are not detectably activated as in (E), but for the WWNR library. (G) Quantitative evaluation of C.PvuII-activated variants from WWNW (panel C) or WWNR (panel D) libraries. CAT levels were measured either in the presence of physiological steady-state levels of C.PvuII (pvuIIC under native control on plasmid pDK200; black bars), or without pvuIIC (white bars). CAT levels were determined via triplicate immunoassays as described in Material and Methods section. For comparison, mutants with inactive OR (WWRR) or OL (RRWW) were also analyzed. pKK represents vector (pKK232-8) control. The error bars indicate SDs.