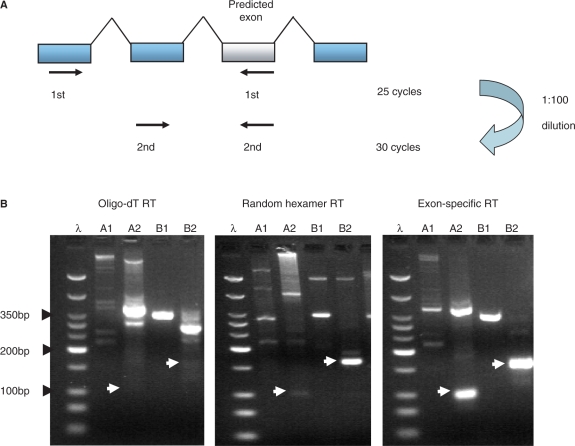
Figure 2.
Semi-nested PCR is more sensitive at detecting exons using exon-specific primed cDNA templates than with either random hexamer or oligo-dT primed templates. (A) Semi-nested PCRs were designed specifically for two rounds of PCRs. Thirty cycles of first round of PCR with an ‘external’ forward primer targeted to a 5′ upstream canonical exonic sequence and used with a reverse primer targeted to the alternative cassette exon. Twenty-five cycles of the second round PCR then uses an ‘internal’ forward primer targeted to an exonic region between the ‘external’ forward primer and the previously used reverse exon primer. A 1:100 dilution of the first round reaction is used as a template for the second round reaction. (B) Two alternative exons tested with the flanking PCR approach and the two different methods RT. A1 and A2 are the first and second PCR reactions for the alternative exon in the ABI1 gene. B1 and B2 are the first and second PCR reactions for the alternative exon in the NCOA2 gene (See supplementary table A for the full list of genes). The expected PCR product sizes for the second round reactions are shown with white arrowheads, The oligo-dT primed experiment did not detected either of the alternative exons (lanes A2 and B2) in comparison to the random hexamer primed experiment that detected the second exon (lane B2) and the exon-specific primed experiment that detected both exons (lanes A2 and B2). DNA ladder λ shows 50 bp, 75 bp, 100 bp, then 50 bp increments to 350 bp, then 500 bp and 766 bp. The strongest band represents 200 bp.